Network enumeration is the process of gathering information about network configurations, connectivity, and active hosts. This is crucial for both network troubleshooting and cybersecurity assessments.
Below are essential commands used for network enumeration.
- [IP Configuration] List all network interfaces
- [IP Configuration] Display full configuration information
- [IP Configuration] Release the IPv4 address for the specified adapter
- [IP Configuration] Release the IPv6 address for the specified adapter
- [IP Configuration] Renew the IPv4 address for the specified adapter
- [IP Configuration] Renew the IPv6 address for the specified adapter
- [IP Configuration] Display the contents of the DNS Resolver Cache
- [IP Configuration] Purge the DNS Resolver Cache
- [IP Configuration] Refresh all DHCP leases and register DNS names
- [Ping] Check communication or connectivity of a computer
- [Ping] Ping indefinitely
- [Ping] Specify the number of echo requests to send
- [Ping] Adjust the size of the ping packet
- [Traceroute] Trace the route to the specified IP
- [Pathping] Trace network latency and packet loss
- [ARP] Display the ARP cache
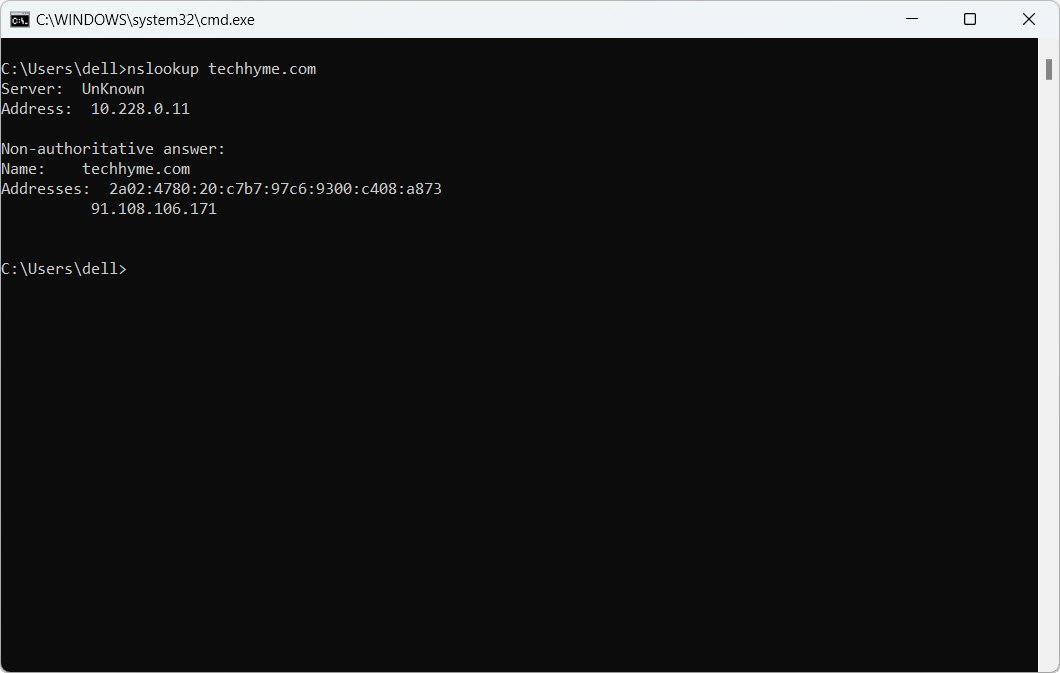
- [Nslookup] Find the hostname associated with an IP address
- [Nslookup] Find the IP address
- [Route] List the current routing table
- [Netstat] Display active connections numerically
- [Netstat] Display all active connections and listening ports numerically
- [Netstat] Display all active connections with process IDs
- [Netstat] Show TCP connections with process information
- [Netstat] Show UDP connections with process information
- [Netstat] Display network connections with the associated executable
- [Netstat] Show all active connections, listening ports, and associated executables
IP Configuration
The ipconfig command is used to display and manage network configurations on a Windows machine.
1. List all network interfaces:
ipconfig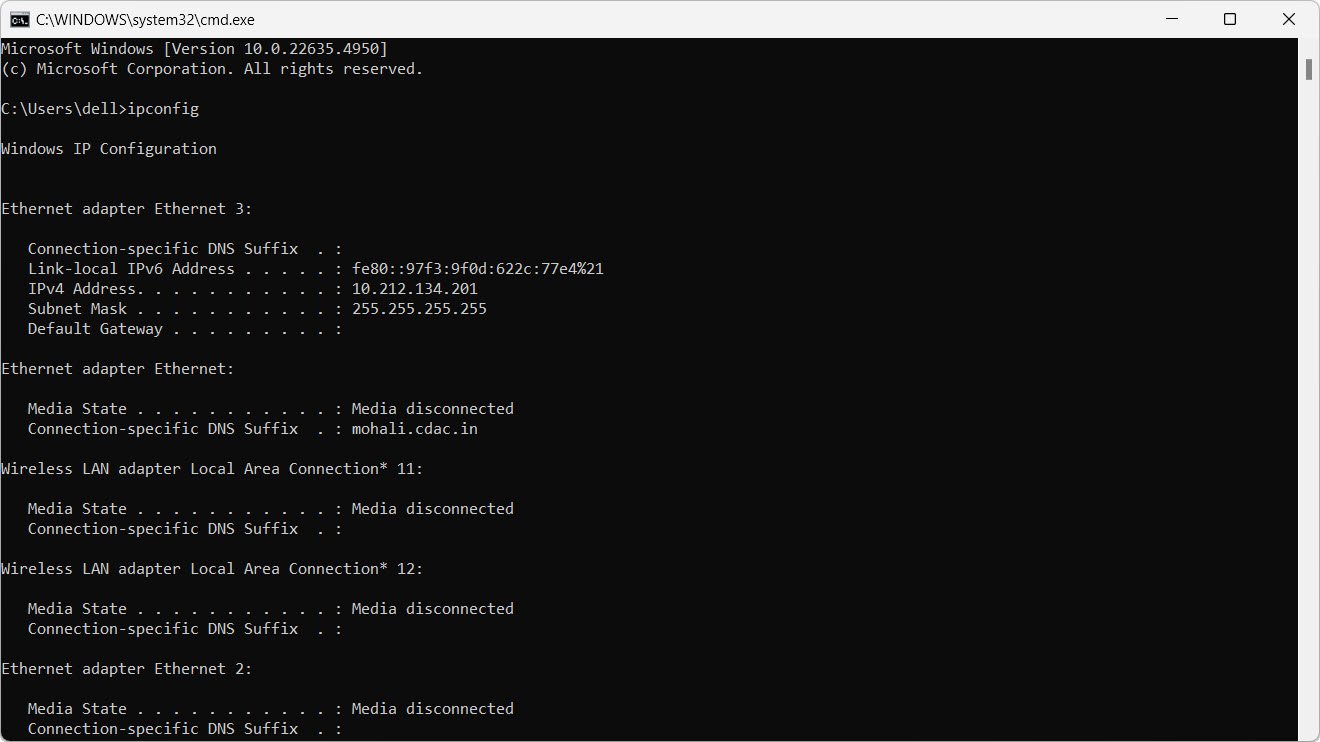
2. Display full configuration information:
ipconfig /all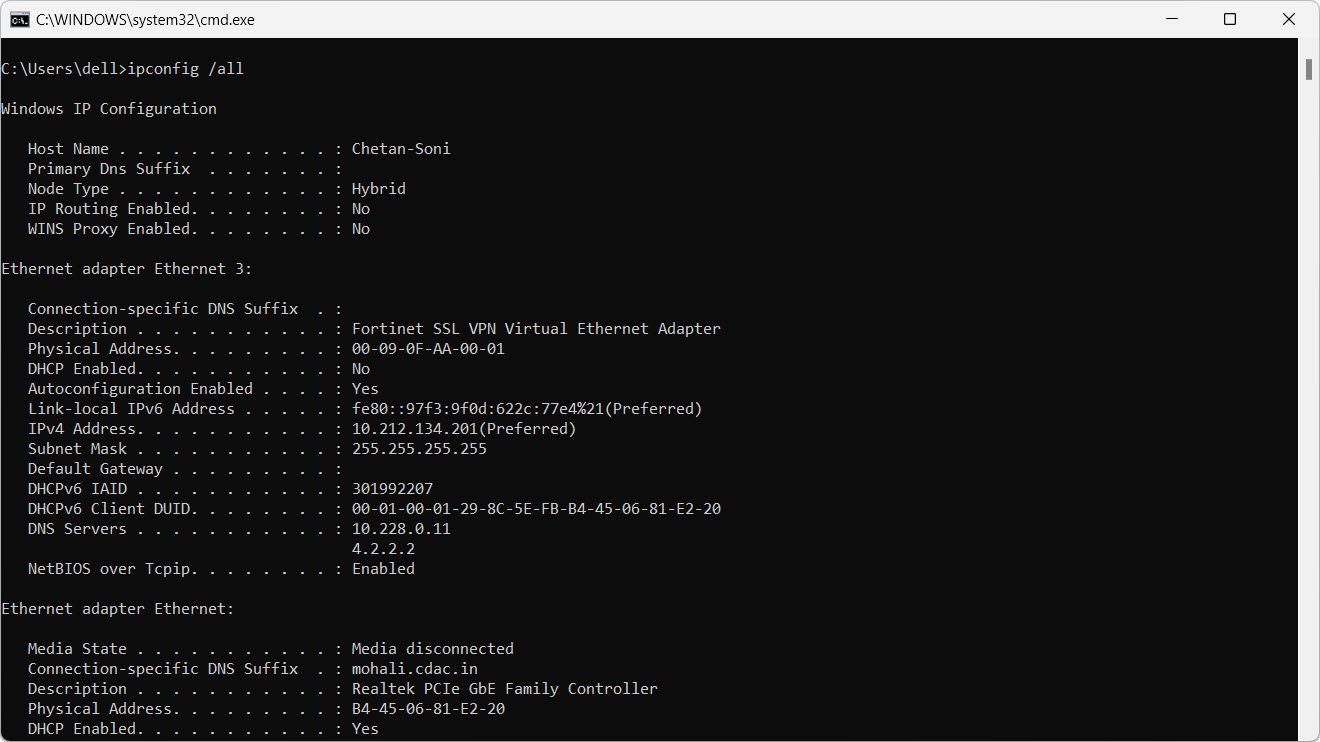
3. Release the IPv4 address for the specified adapter:
ipconfig /release4. Release the IPv6 address for the specified adapter:
ipconfig /release65. Renew the IPv4 address for the specified adapter:
ipconfig /renew6. Renew the IPv6 address for the specified adapter:
ipconfig /renew67. Display the contents of the DNS Resolver Cache:
ipconfig /displaydns
8. Purge the DNS Resolver Cache:
ipconfig /flushdns9. Refresh all DHCP leases and register DNS names:
ipconfig /registerdnsPing
The ping command is used to check communication or connectivity between computers.
10. Check communication or connectivity of a computer:
ping 192.168.1.6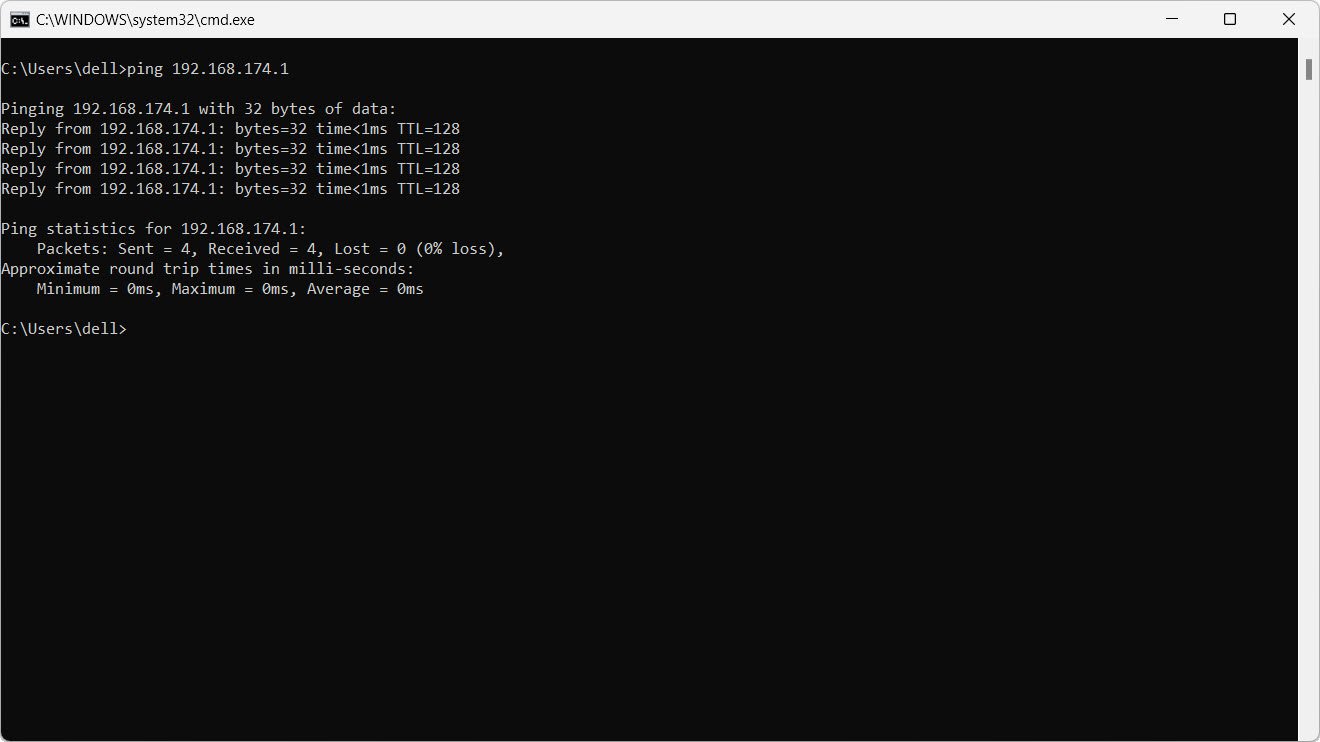
11. Ping indefinitely:
ping 192.168.1.6 -t
12. Specify the number of echo requests to send:
ping -n 1 192.168.1.613. Adjust the size of the ping packet:
ping -n 1 -l 65500 192.168.1.6Traceroute
The tracert command traces the path or route to a specified remote host.
14. Trace the route to the specified IP:
tracert 192.168.1.6
Pathping
The pathping command combines the features of ping and tracert, providing information on network latency and packet loss.
15. Trace network latency and packet loss:
pathping 8.8.8.8
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol)
The arp command is used to view and manage the ARP cache.
16. Display the ARP cache:
arp -a
NSLookup
The nslookup command allows users to look up DNS-related information.
17. Find the hostname associated with an IP address:
nslookup 192.168.1.33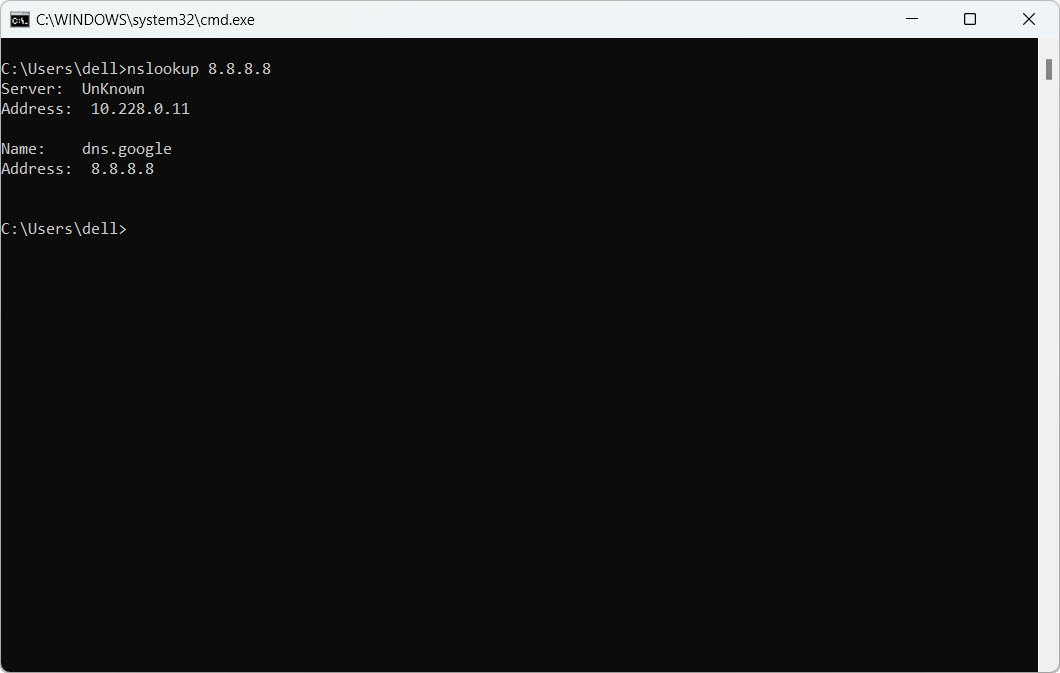
18. Find the IP address associated with a domain name:
nslookup armour.comRoute Table
The route command is used to manipulate the IP routing table.
19. List the current routing table:
route print
Netstat
The netstat command displays network statistics, connections, and routing tables.
20. Display active connections numerically:
netstat -n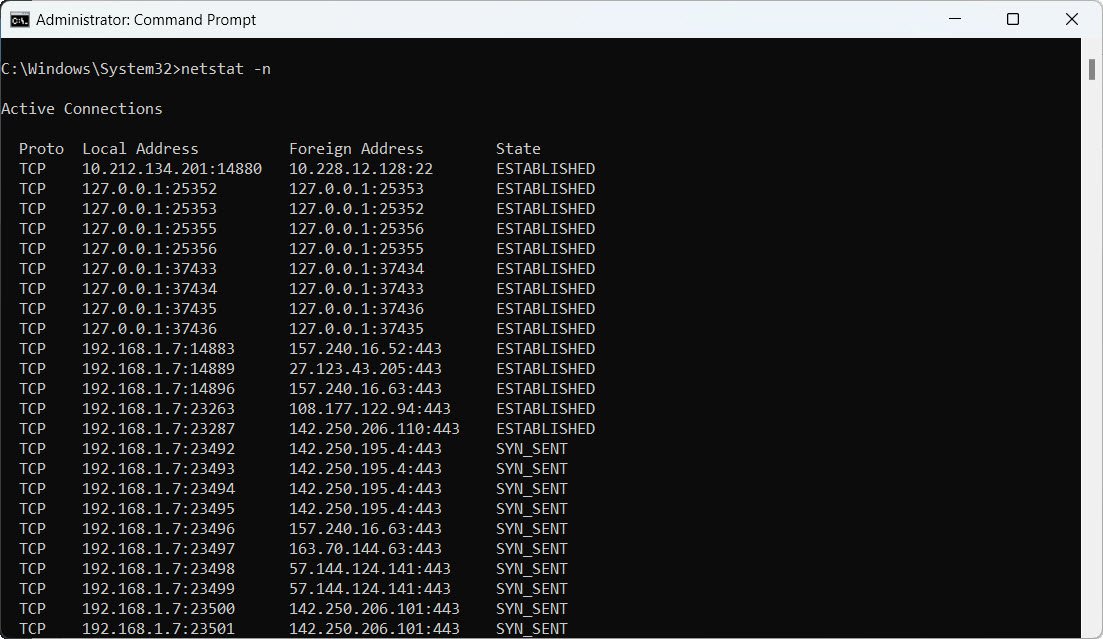
21. Display all active connections and listening ports numerically:
netstat -an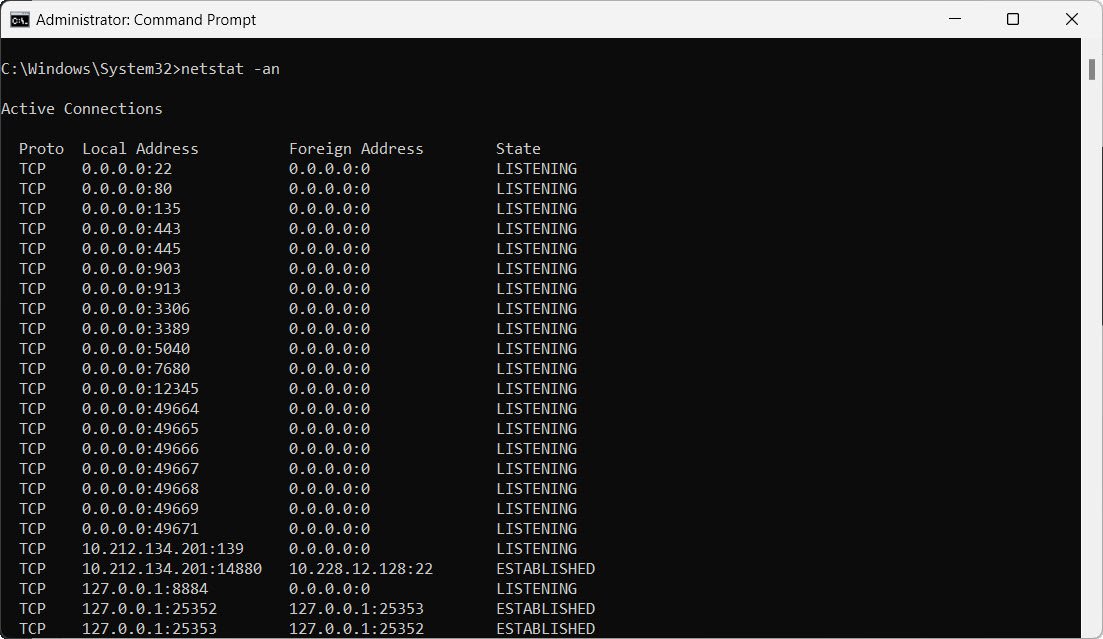
22. Display all active connections with process IDs:
netstat -ano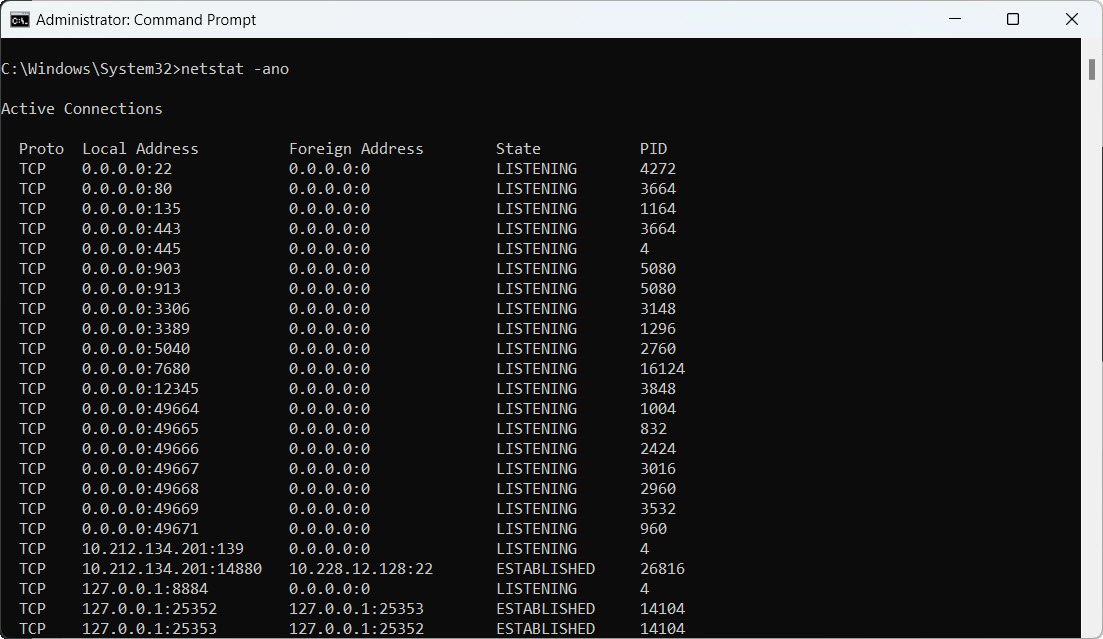
23. Show TCP connections with process information:
netstat -anop tcp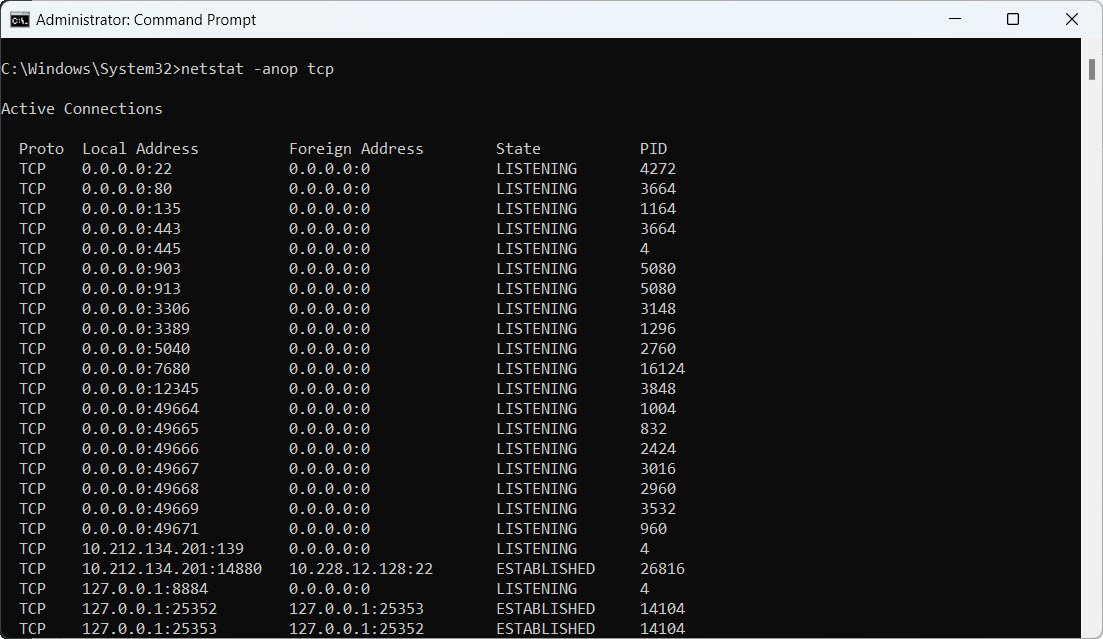
24. Show UDP connections with process information:
netstat -anop udp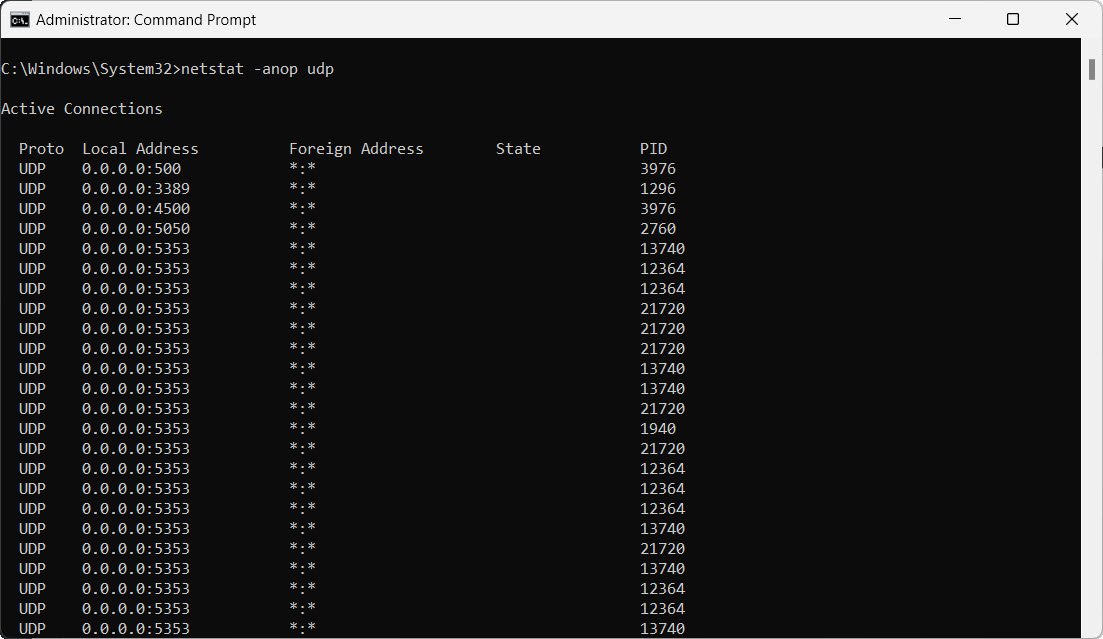
25. Display network connections with the associated executable:
netstat -nob
26. Show all active connections, listening ports, and associated executables:
netstat -anob
Conclusion
Network enumeration is a crucial part of network administration and security assessments. Using the above commands, IT professionals can diagnose network issues, optimize performance, and enhance security measures.
Regularly auditing network configurations and monitoring active connections help prevent potential vulnerabilities and ensure a secure network environment.