The duf utility is nothing but an enhancement of what du and df commands do to check used and free space in a structured and eye-pleasing way. Duf is one of the new CLI tools that is gaining quite some popularity among Linux users.
To install duf on Ubuntu, you can use the apt package manager:
Command: apt install duf
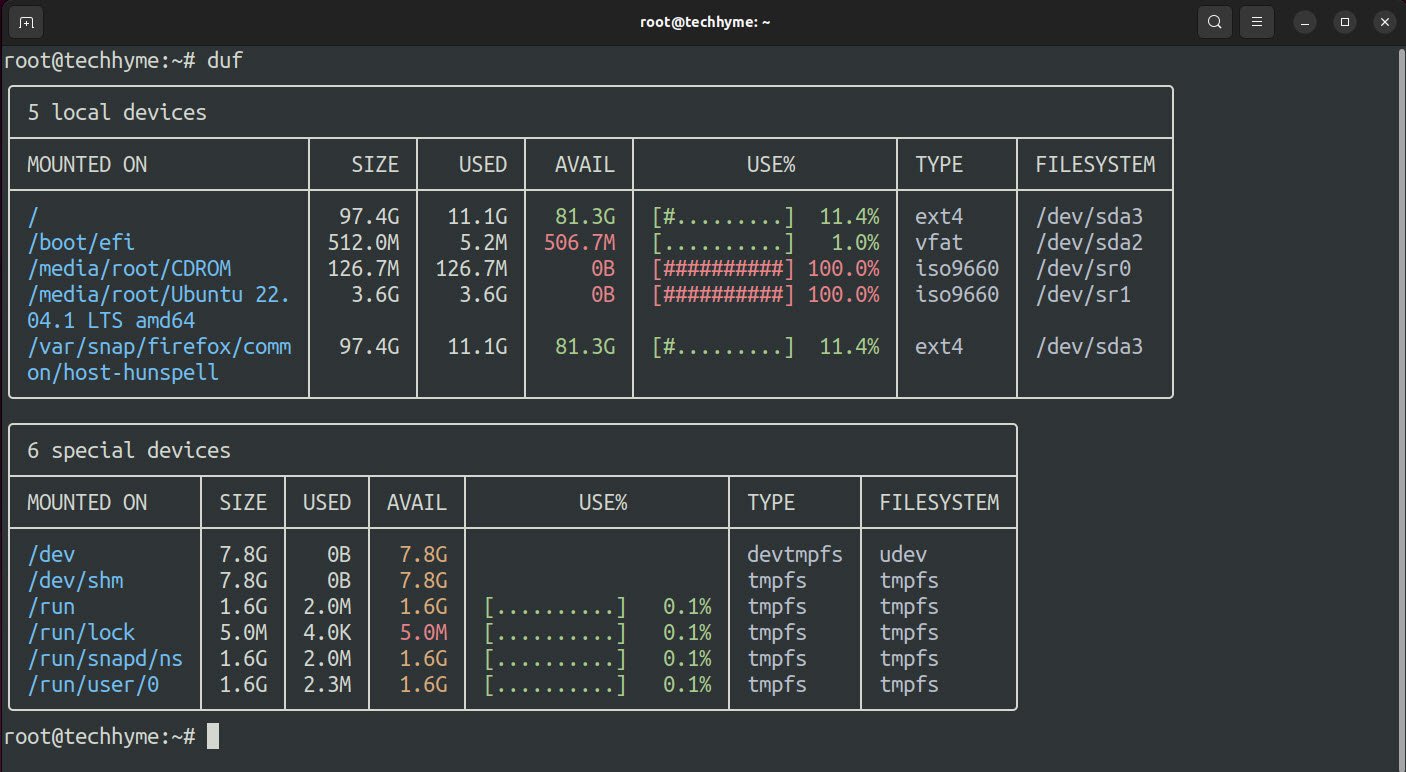
You can simply use duf without any options and it will get you a list of mounted devices:
Command: duf
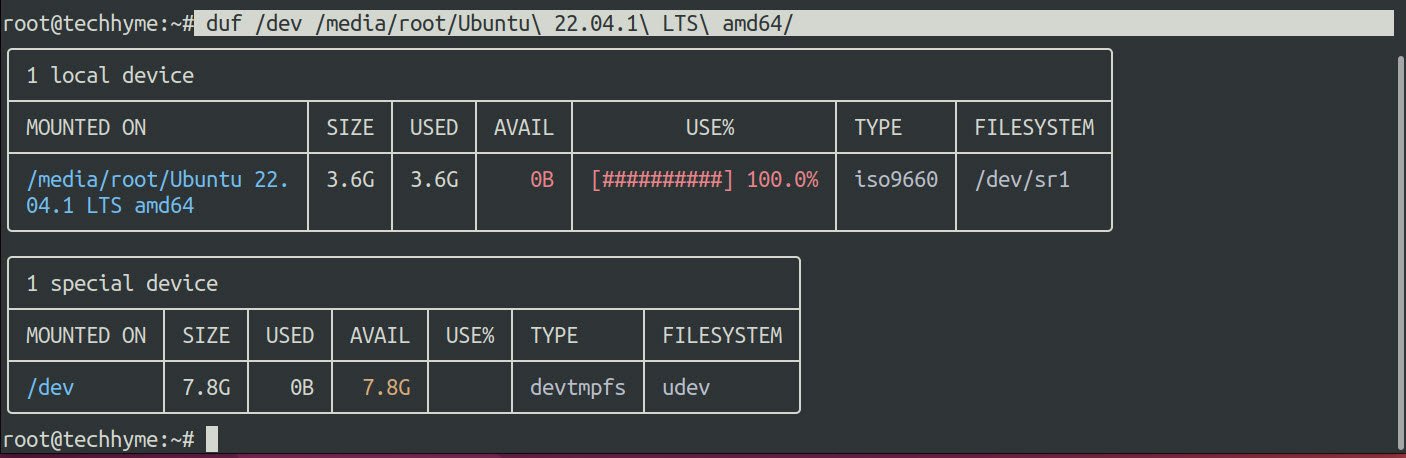
You can use duf to list one or more devices at the same time. You just have to specify the path of the mounting port or device and that’s it:
Command: duf /dev /media/root/Ubuntu 22.04.1 LTS amd64/
The duf utility provides various options so that you can filter output and have intended results. For instance, you can the –only option to show only specific devices:
Command: duf –only local
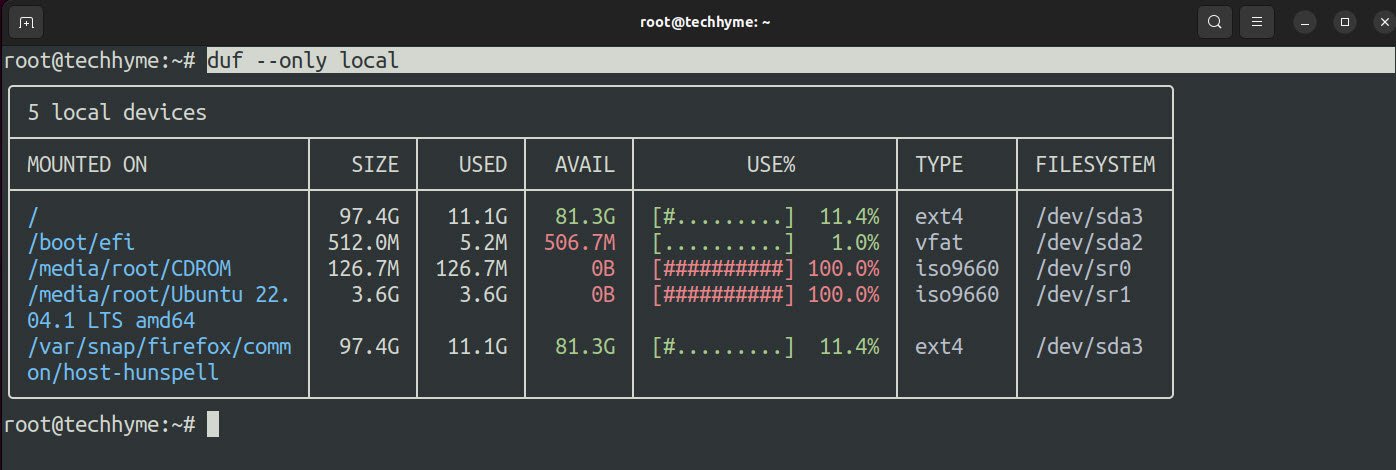
And if you want to list specific filesystems, you can use –only-fs and append filesystem types.
Command: duf –only-fs tmpfs
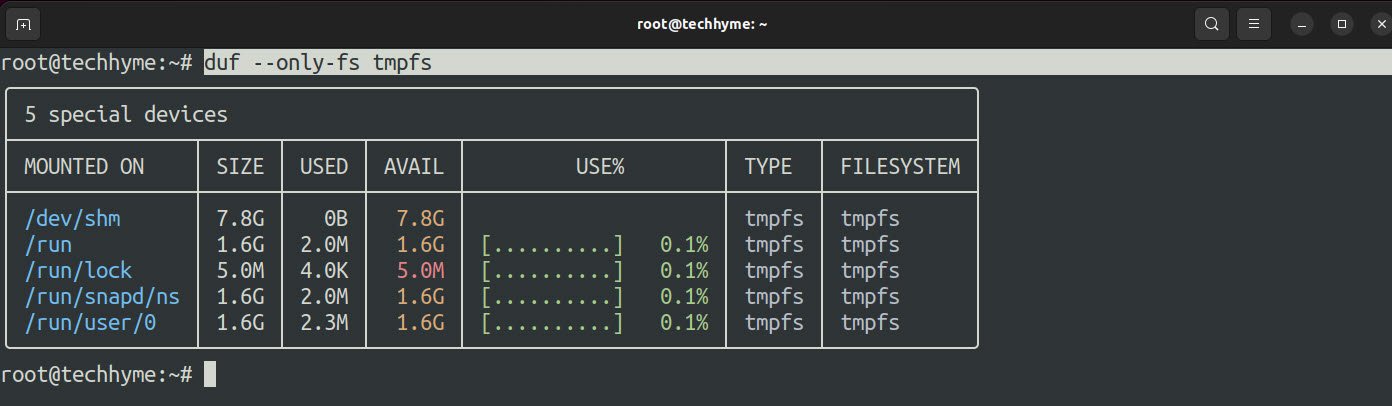
Furthermore, you can also sort the output based on a variety of keys such as size, usage, and more using the –sort option.
Command: duf –sort usage
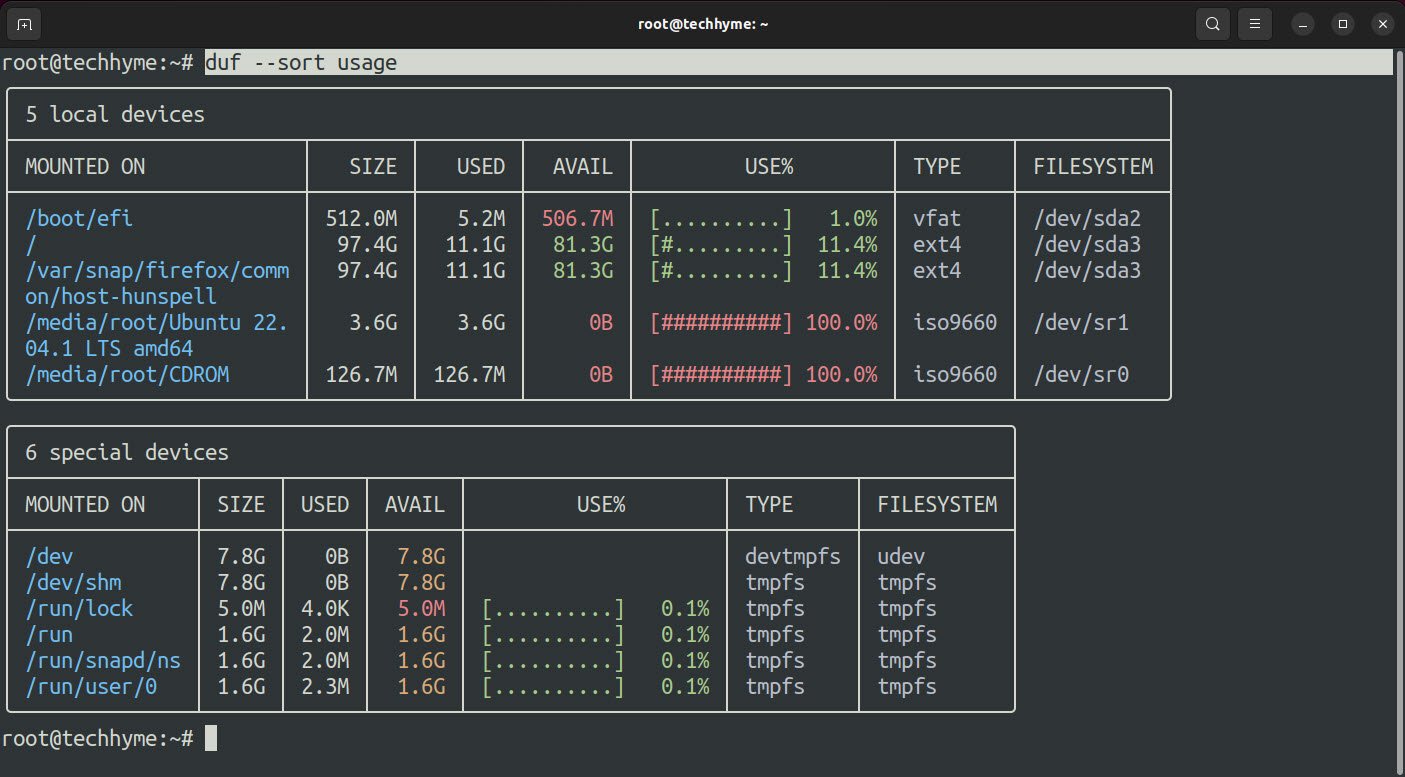
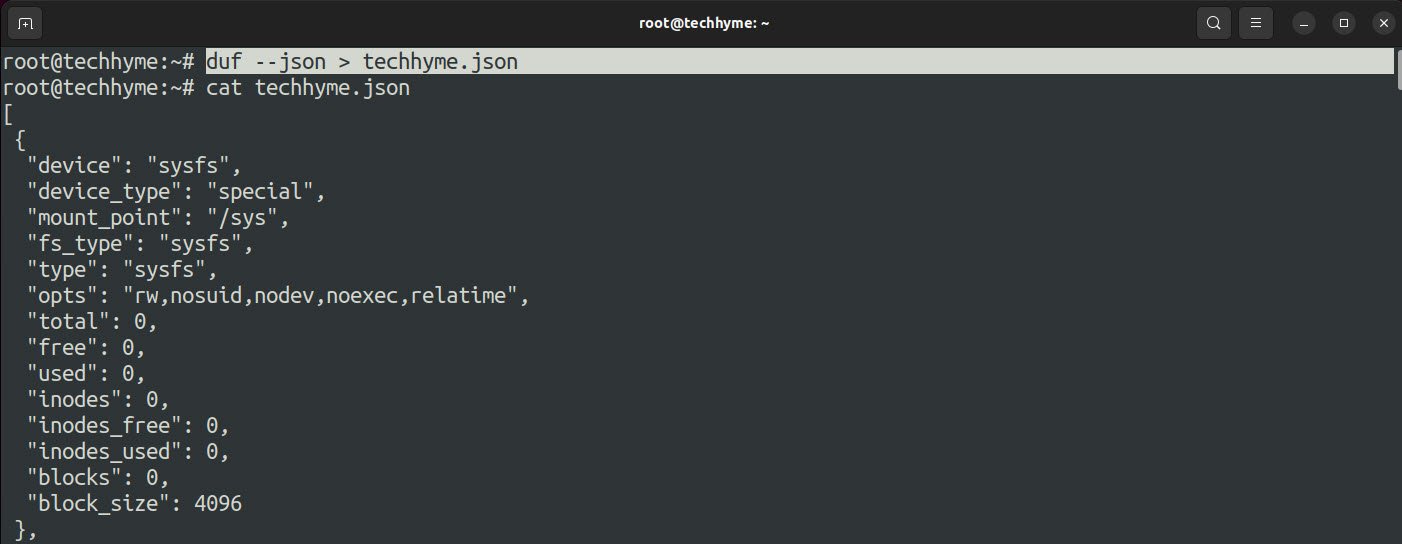
If you want the output in JSON format, then you can use –json option:
Command: duf –json
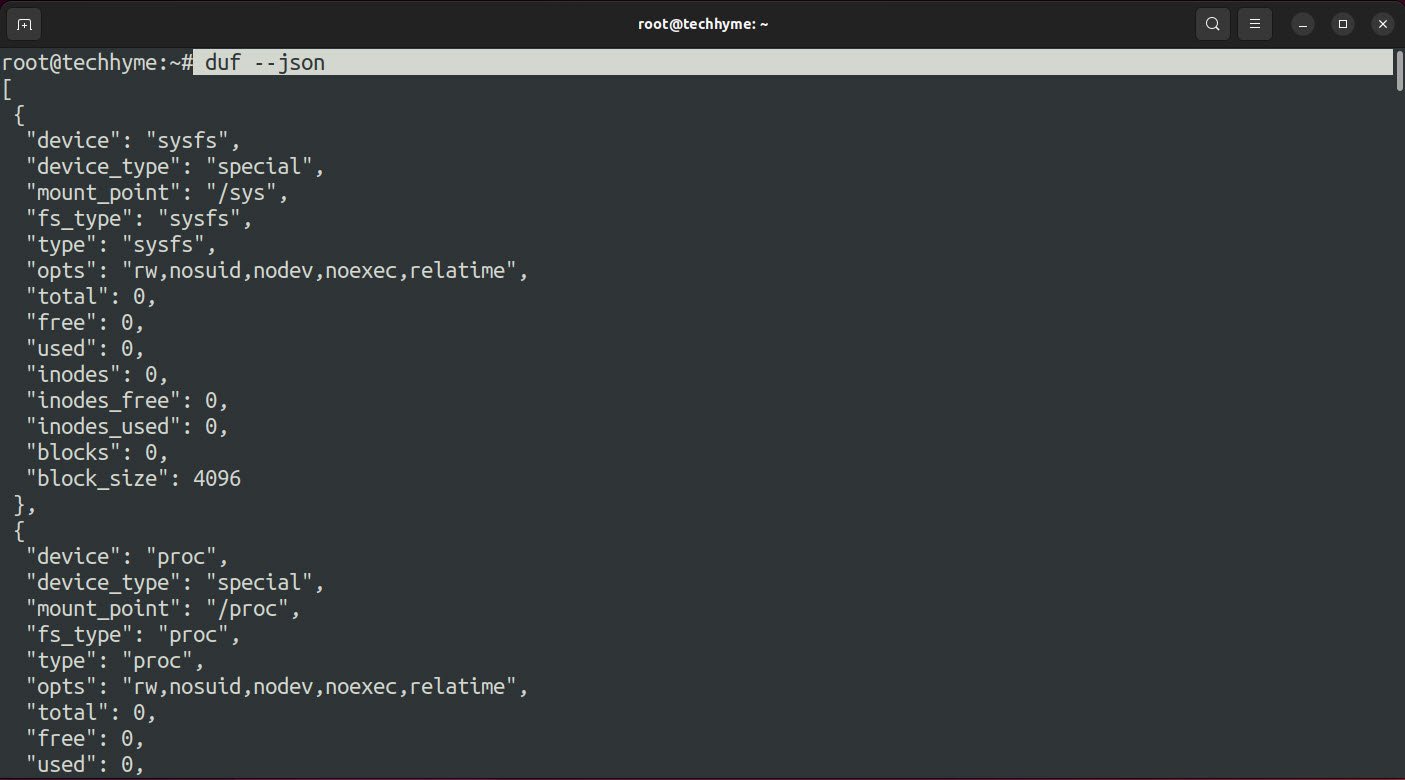
In case, if you want to save the output in a text file, you can redirect the standard output to the text file:
Command: duf –json > techhyme.json