In our interconnected world, where communication transcends geographical boundaries and data flows seamlessly across devices, understanding network fundamentals is more critical than ever. Networks serve as the backbone of modern and digital society, enabling businesses, governments, and individuals to collaborate, share information, and access resources.
But what exactly are network fundamentals? These foundational principles form the bedrock upon which all network architectures are built. From the smallest home network to sprawling global infrastructures, these concepts remain constant. They encompass protocols, devices, addressing schemes, and network topologies—the essential building blocks that allow data to traverse the digital highways.
Whether you’re an aspiring IT professional, a curious student, or simply someone intrigued by the inner workings of networks, the below set of important questions covers it all.
1. Which of these devices uses a MAC address to make forwarding decisions?
(A) Hub
(B) Switch
(C) Router
(D) Bridge
2. IP addresses can be found at which layer of the OSI model?
(A) Network layer
(B) Data-link layer
(C) Application layer
(D) Session layer
3. What type of transmission is sent to all devices on a subnet?
(A) Broadcast
(B) AllCast
(C) Anycast
(D) Unicast
4. The ability to transmit data in both directions but only in one direction at a time is known as what?
(A) Simplex
(B) Full duplex
(C) Uniplex
(D) Half-duplex
5. What type of network could be described as an internal internet?
(A) Perimeter network
(B) Extranet
(C) Intranet
(D) DMZ
6. What type of network allows trusted partners to have access to limited internal resources?
(A) Perimeter network
(B) Extranet
(C) Intranet
(D) DMZ
7. What term describes a network that covers a small geographical area?
(A) LAN
(B) MAN
(C) CAN
(D) SAN
8. Which of these is a private Class B IP address?
(A) 172.15.56.23
(B) 172.31.56.23
(C) 172.33.56.23
(D) 192.168.56.23
9. Which of these is a valid MAC address?
(A) A6:8G:EE:12:C6:89
(B) B9:DA:00:12:78:34:09:EE:D2
(C) A698::0976:AD5B:F78A
(D) AA:6F:7A:BB:C3:9D
10. Which of these is a WAN technology that breaks data down into smaller chunks and does not use a fixed path to the destination network?
(A) Packet switching
(B) Frame Relay
(C) ISDN
(D) ADSL
11. The point where services from your service provider interface with your own services is known as what?
(A) Hub
(B) POTS
(C) Demarcation point
(D) ISDN
12. Which Windows command-line tool will output a list of routers that your data traverses?
(A) ping
(B) ipconfig
(C) traceroute
(D) tracert
13. Which of the following provides a dedicated connection between your premises and another location?
(A) POTS
(B) ADSL
(C) Leased line
(D) ISDN
14. Which of these IEEE standards covers Wi-Fi?
(A) 802.3
(B) 802.5
(C) 802.11
(D) 802.16
15. What access methodology is used by Wi-Fi?
(A) CSMA/CA
(B) CSMA/CD
(C) Token ring
(D) STP
16. What is the third step of the DHCP process?
(A) Acknowledge
(B) Request
(C) Discover
(D) Offer
17. Which of these Wi-Fi standards use MIMO?
(A) 802.11a
(B) 802.11b
(C) 802.11g
(D) 802.11n
18. Which network topology provides the greatest redundancy?
(A) Mesh
(B) Bus
(C) Star
(D) Ring
19. Look at the topology in the following diagram:

How many broadcast domains and how many collision domains are there?
(A) 1 x Broadcast domains and 7 x collision domains
(B) 2 x Broadcast domains and 7 x collision domains
(C) 1 x Broadcast domains and 10 x collision domains
(D) 2 x Broadcast domains and 10 x collision domains
20. What is the maximum length of a Cat 5 cable?
(A) 100 m
(B) 185 m
(C) 200 m
(D) 500 m
21. What type of cable should be used in HVAC?
(A) Unshielded twisted pair
(B) Plenum
(C) Fiber optic
(D) Shielded twisted pair
22. Look at the simple topology in the following diagram and the accompanying screenshot of the MAC table on the switch:
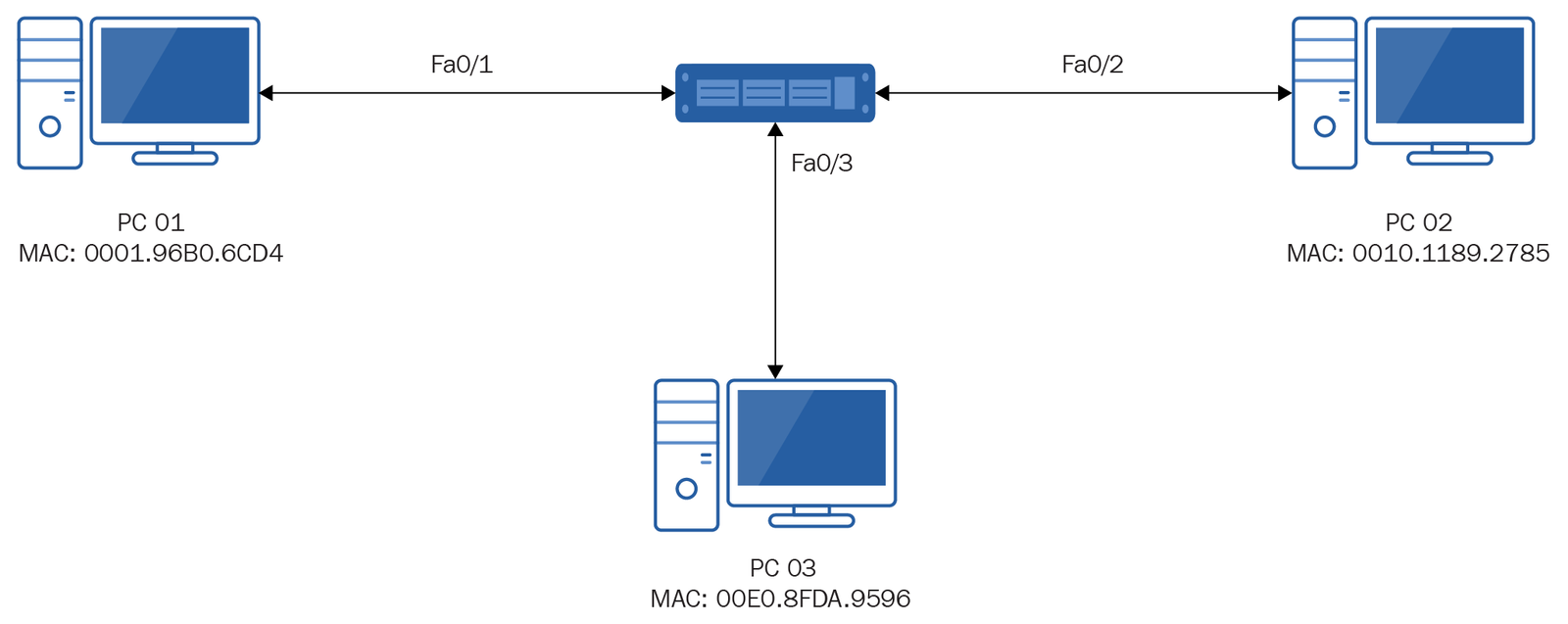
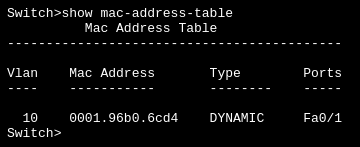
PC 02 sends some data destined for PC 01. What would the switch do after receiving the data from PC 02?
(A) Forward the data through port Fa0/1 to PC 01.
(B) Forward the data out of ports FA0/1 and Fa0/3.
(C) Update the MAC table with the MAC address and port number for PC 02.
(D) Discard the data.
(E) Sends it out to all ports
23. What can be used to avoid broadcast storms?
(A) RIP
(B) OSPF
(C) STP
(D) IS-IS
24. What does a router look at to determine the correct interface to forward data through?
(A) Hop count
(B) Bandwidth
(C) Jitter value
(D) Metric
25. RIP is an example of what type of routing vector?
(A) Link-state vector
(B) Distance vector
(C) Hybrid vector
(D) Shortest path vector
26. Thicknet cable is also referred to as what?
(A) 10baseT
(B) 10base2
(C) 10base5
(D) 10baseTx
27. To avoid network bounce, what should be used with a bus topology?
(A) BNC
(B) Terminator
(C) RJ-45
(D) Vampire tap
28. Which layer of the OSI model is responsible for encryption?
(A) Application layer
(B) Presentation layer
(C) Session layer
(D) Transport layer
29. Which of these protocols would you find at the transport layer of the OSI model?
(A) HTTP
(B) POP3
(C) IMAP
(D) UDP
30. Port number 1400 falls under what range of ports?
(A) Registered ports
(B) Well known ports
(C) Ephemeral ports
(D) Dynamic ports
31. You need to allow SMTP traffic through your firewall. What port should you open?
(A) 21
(B) 22
(C) 23
(D) 25
32. Which of these is NOT a layer of the TCP/IP model?
(A) Application
(B) Presentation
(C) Network
(D) Transport
33. Which of these services runs on port 23?
(A) Telnet
(B) FTP
(C) POP3
(D) DNS
34. Which of these is the IPv6 loopback address?
(A) 127.0.0.1
(B) ::1
(C) 127::1
(D) FE80::1
35. Which of these is a valid IPv6 address?
(A) 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334
(B) 20:01:0d:b8:85:a3
(C) ae03:0d2c:15b3::8a2g:0370:7334
(D) 2001::85a3::8a2e:0370:7334
36. What type of transmission sends data to the nearest device providing a particular service?
(A) Nearcast
(B) Unicast
(C) Anycast
(D) Broadcast
37. Which of these a link-local IPv6 address?
(A) 2000::/3
(B) ff00::/8
(C) fe80::/10
(D) ::1
38. A user complains their device cannot connect to a resource using a fully qualified domain name but can access it using an IP address. What service should you investigate?
(A) ARP
(B) DNS
(C) DHCP
(D) WINS
39. Billy is a member of the following security groups: Marketing, Finance, Management, and Manchester. Each group has the following share permissions applied to a folder:
Marketing: Read
Finance: Full control
Management: Read
Manchester: Change
What is Billy’s effective share permission?
(A) Read
(B) Change
(C) Read and change
(D) Full control
40. When a user logs on to a device on a domain, where are their credentials sent for authentication?
(A) Domain controller
(B) DNS server
(C) DHCP server
(D) ARP
41. Which of these devices uses IP addresses for forwarding decisions?
(A) Switch
(B) Hub
(C) Router
(D) Bridge
42. Which of these devices is classed as a layer 1 device?
(A) Switch
(B) Hub
(C) Router
(D) Bridge
43. What type of transmission is sent to a predefined group of devices on a network?
(A) Anycast
(B) Multicast
(C) Broadcast
(D) Unicast
44. The ability to transmit data in only one direction is known as what?
(A) Simplex
(B) Half-duplex
(C) Full duplex
(D) Simple duplex
45. A perimeter network is also known as what?
(A) Intranet
(B) DMZ
(C) Extranet
(D) Internet
46. Which of these is a Class D address?
(A) 10.34.56.12
(B) 129.87.98.87
(C) 192.15.8.223
(D) 224.45.34.23
47. Which of these IEEE standards covers Ethernet?
(A) 802.3
(B) 802.5
(C) 802.11
(D) 802.15
48. Which of these IEEE standards covers a token ring?
(A) 802.3
(B) 802.5
(C) 802.11
(D) 802.15
49. At what point during a dynamic IP address lease does the client first attempt to renew the address?
(A) 25% of the lease used
(B) 50% of the lease used
(C) 75% of the lease used
(D) Once the lease expires
50. OSPF is an example of what sort of routing protocol?
(A) Link-state vector
(B) Distance vector
(C) Hybrid vector
(D) Shortest path vector
51. What is the maximum segment length of a thinnet cable?
(A) 100 m
(B) 185 m
(C) 200 m
(D) 500 m
52. You wish to connect to a device to control it via a secure command-line connection. Which service would you use?
(A) Telnet
(B) HTTPS
(C) SSH
(D) SFTP
53. Which of these services resolves NetBIOS names to IP addresses?
(A) DNS
(B) DHCP
(C) ARP
(D) WINS
54. When a computer first sends a discover packet to a DHCP server, what IP address is used as the source IP?
(A) 127.0.0.1
(B) 192.168.0.1
(C) 0.0.0.0
(D) 255.255.255.255
55. You wish to configure a static route from the command line. What switch would you use to ensure the route remained after a system reboot?
(A) -p
(B) -persistent
(C) -remain
(D) -r
56. What is the transmission rate of OC-3?
(A) 10 Mbps
(B) 51.84 Mbps
(C) 155.52 Mbps
(D) 622.08 Mbps
57. Which technology does the term POTS refer to?
(A) Dial-up
(B) Fiber optic networking
(C) Satellite networking
(D) PAN networking
58. You are testing a server and need to communicate to it by its FQDN, but want to restrict the name resolution to just one device. What would you do?
(A) Configure a PTR record on the DNS server.
(B) Configure the LMHOSTS file.
(C) Configure an alias on the DNS server.
(D) Configure the HOSTS file.
59. Rather than pointing to an IP address, a DNS record points to another FQDN. What type of record is this?
(A) PTR
(B) CNAME
(C) SRV
(D) NS
60. What type of DNS record would you find in a reverse lookup zone?
(A) PTR
(B) CNAME
(C) SRV
(D) NS
61. Which of these is NOT an alternative representation of the following IPv6 address? 2001:0000:3238:DFE1:0063:0000:0000:FEFB
(A) 2001:0:3238:DFE1:063::FEFB
(B) 2001::3238:DFE1:63:0:0:FEFB
(C) 2001::3238:DFE1:0063::FEFB
(D) 2001:0:3238:DFE1:63:0:0:FEFB
62. The first six characters of a MAC address represent what?
(A) Network ID
(B) OUI
(C) CPU type
(D) Maximum bandwidth
63. A client opens up port 2031 and connects to an FTP server on port 21. The client then informs the FTP server it is running in PASV mode. What port would the server open to receive the data being transferred?
(A) 20
(B) 2032
(C) 21
(D) A random port selected by the server itself
64. You have a wireless access point that supports IEEE802.11b and IEEE 802.11g. What would happen if you added an 802.11b device to this network?
(A) The speed of the 802.11b device would increase to 54 Mbps.
(B) The speed of the network would drop down to 11 Mbps.
(C) The 802.11b device would still communicate at 11 Mbps, and the 802.11g devices would still communicate at 54 Mbps.
(D) The access type would change to CSMA/C(D)
65. What command would you run to show the MAC address of a network interface?
(A) ipconfig /all
(B) ipconfig
(C) ipconfig /getmac
(D) ipconfig /displaymac
66. Which of these technologies uses 2 x B channels and 1 x D channel?
(A) PRI
(B) Satellite
(C) Dial-up
(D) BRI
67. How long is an IPv6 address?
(A) 32 bits
(B) 48 bits
(C) 128 bits
(D) 256 bits
68. Which of these Wi-Fi encryption standards requires the use of a RADIUS server?
(A) WEP
(B) WPA
(C) WPA2-PSK
(D) WPA2-enterprise
69. At which layer of the OSI model would you find frames?
(A) Transport layer
(B) Data-link layer
(C) Application layer
(D) Session layer
70. Which network topology requires a central hub or device?
(A) Mesh
(B) Ring
(C) Bus
(D) Star
71. You wish to configure NTFS permissions on a folder but the security tab is not visible in the properties. What is the most likely reason for this?
(A) The folder is on a FAT partition.
(B) You do not have the appropriate permissions.
(C) NTFS permissions can only be applied to files.
(D) The folder is encrypted.
72. You wish to create a hidden share. Which of these would you suffix to the share name to create this?
(A) %
(B) *
(C) $
(D) !
73. What is the MAC table on a switch also referred to as?
(A) CAM table
(B) ARP table
(C) RARP table
(D) NAT table
74. The ping command is part of which suite of tools?
(A) HTTP
(B) TLS
(C) ICMP
(D) ARP
75. You believe your PC has cached an old IP to name resolution. What command would you run as part of this process to alleviate this issue?
(A) ipconfig /releasedns
(B) ipconfig /flushdns
(C) ipconfig /cleardnscache
(D) ipconfig /cleandns
76. When creating a cross over cable, which pins would you need to rewire compared to a straight-through cable?
(A) 1, 2, 3, 4
(B) 4, 5, 6, 7
(C) 3, 5, 7, 8
(D) 1, 2, 3, 6
77. What connector would you use with a telephone line?
(A) RJ-45
(B) RJ-11
(C) BNC
(D) Vampire tap
78. The process of connecting two adjacent channels on a Wi-Fi device is known as what?
(A) NIC teaming
(B) Channel bonding
(C) NIC bonding
(D) MIMO
79. What Windows command would you run to identify all of the routers that your data transits through to reach its final destination?
(A) route print
(B) ping
(C) tracert
(D) show route
80. A firewall that keeps track of all outgoing connections, hence blocking unsolicited traffic, is known as what type of firewall?
(A) Stateful
(B) Stateless
(C) Dynamic
(D) Heuristic
Correct Answers –
- (B) Switch
- (A) Network layer
- (A) Broadcast
- (D) Half-duplex
- (C) Intranet
- (B) Extranet
- (A) LAN
- (B) 172.31.56.23
- (D) AA:6F:7A:BB:C3:9D
- (A) Packet switching
- (C) Demarcation point
- (D) tracert
- (C) Leased line
- (C) 802.11
- (A) CSMA/CA
- (B) Request
- (D) 802.11n
- (A) Mesh
- (B) 2 x Broadcast domains and 7 x collision domains
- (A) 100 m
- (B) Plenum
- (C) Update the MAC table with the MAC address and port number for PC 02
- (C) STP
- (D) Metric
- (B) Distance vector
- (C) 10base5
- (B) Terminator
- (B) Presentation layer
- (D) UDP
- (A) Registered ports
- (D) 25
- (B) Presentation
- (A) Telnet
- (B) ::1
- (A) 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334
- (C) Anycast
- (C) fe80::/10
- (B) DNS
- (D) Full control
- (A) Domain controller
- (C) Router
- (B) Hub
- (B) Multicast
- (A) Simplex
- (B) DMZ
- (D) 224.45.34.23
- (A) 802.3
- (B) 802.5
- (B) 50% of the lease used
- (A) Link-state vector
- (B) 185 m
- (C) SSH
- (D) WINS
- (C) 0.0.0.0
- (A) -p
- (C) 155.52 Mbps
- (A) Dial-up
- (D) Configure the hosts file.
- (B) CNAME
- (A) PTR
- (C) 2001::3238:DFE1:0063::FEFB
- (B) OUI
- (D) A random port selected by the server itself
- (B) The speed of the network would drop down to 11 Mbps
- (A) ipconfig /all
- (D) BRI
- (C) 128 bits
- (D) WPA2-enterprise
- (B) Data-link layer
- (D) Star
- (A) The folder is on a FAT partition
- (C) $
- (A) CAM table
- (C) ICMP
- (B) ipconfig /flushdns
- (D) 1, 2, 3, 6
- (B) RJ-11
- (B) Channel bonding
- (C) tracert
- (A) Stateful








