MariaDB is an open-source relational database management system (RDBMS) that is a fork of the popular MySQL database. It was created as a result of concerns regarding the acquisition of MySQL by Oracle Corporation. The original developers of MySQL, led by Michael “Monty” Widenius, created MariaDB to ensure the continuity and open development of a compatible database system.
MariaDB aims to provide a drop-in replacement for MySQL, meaning it is designed to be functionally compatible with MySQL and can be used as a direct substitute without requiring significant modifications to applications or code. It offers enhanced performance, scalability, and additional features compared to MySQL. MariaDB is widely used in various applications and is supported by a large and active community of developers and contributors.
Installation of MariaDB in Ubuntu
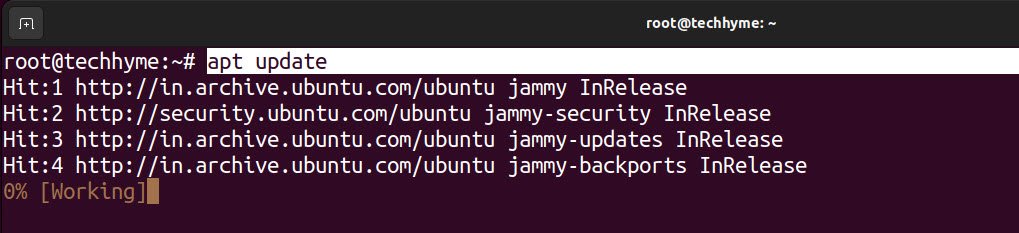
The first step is the execute the “apt update” command which is used to update the package lists of available software packages.
By running this command, your system retrieves the latest information about software updates and new packages from the software repositories configured on your system.
Now you need to configure the APT package repository by running the following command:
Command: wget https://downloads.mariadb.com/MariaDB/mariadb_repo_setup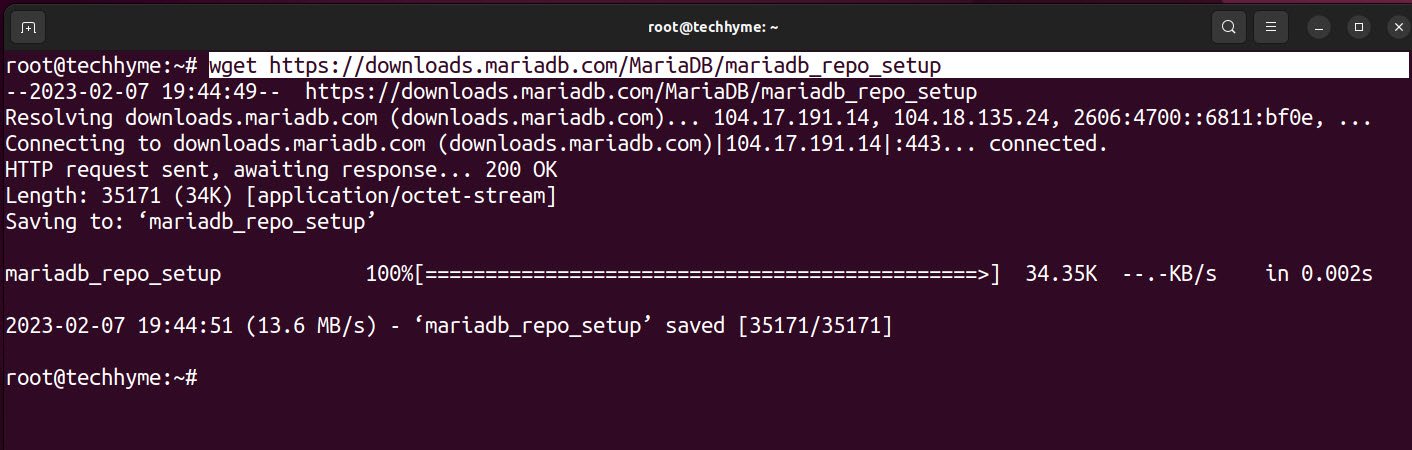
Grant the execution privileges by running “chmod +x mariadb_repo_steup”

Run the following repo setup file.
Command: ./mariadb_repo_setup
As soon as the repo installation completed, run the apt update command again.

Next step is to install MariaDB Community Server and package dependencies.
Command: apt install mariadb-server mariadb-backup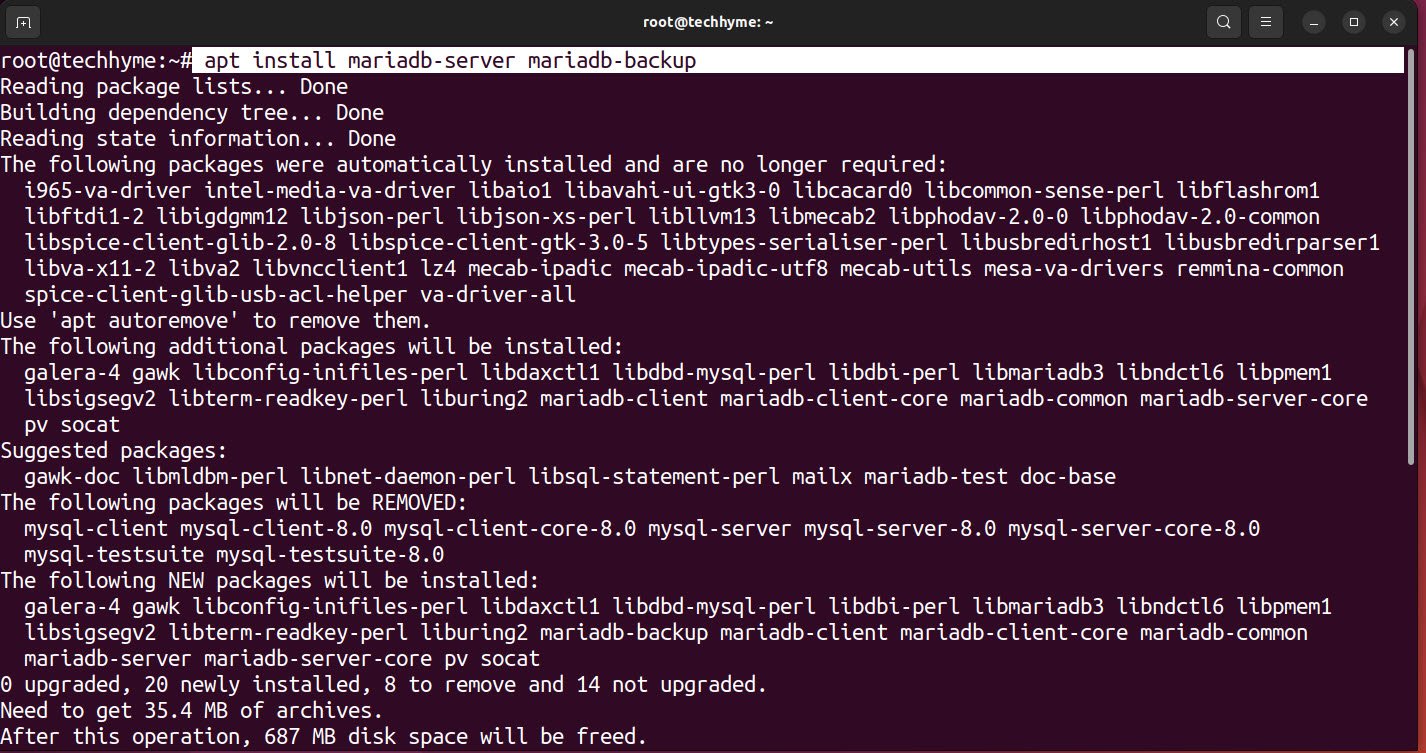
Now start the mariadb service by using systemctl command.
Command: systemctl start mariadb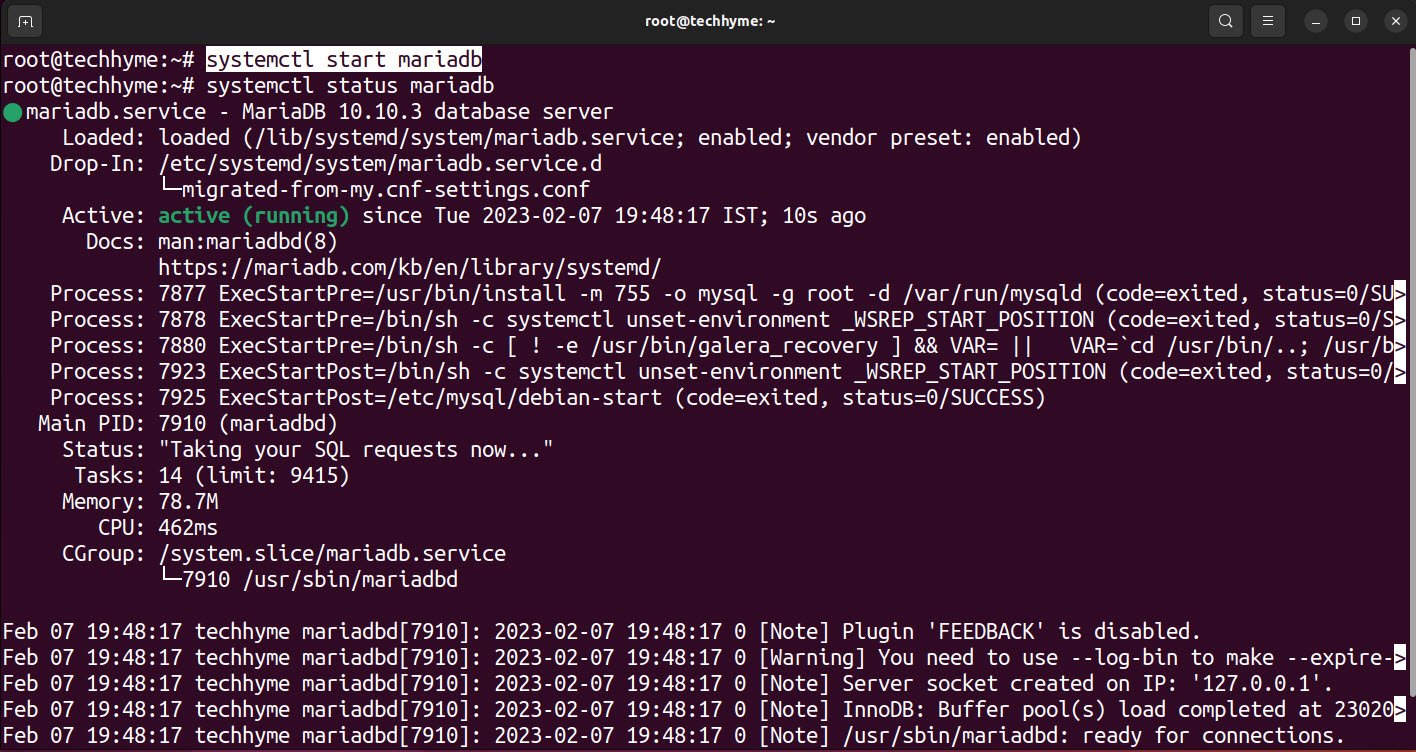
Once you know that it’s running, you can easily connect to it by using the following command:
Command: mariadb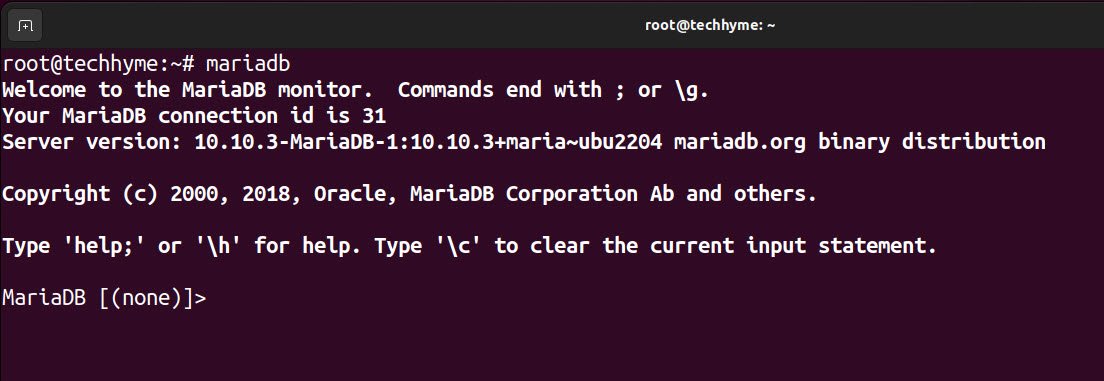
You can also enable the mariadb service at startup so next time you reboot the server, the MariaDB service will start automatically.
Command: systemctl enable mariadb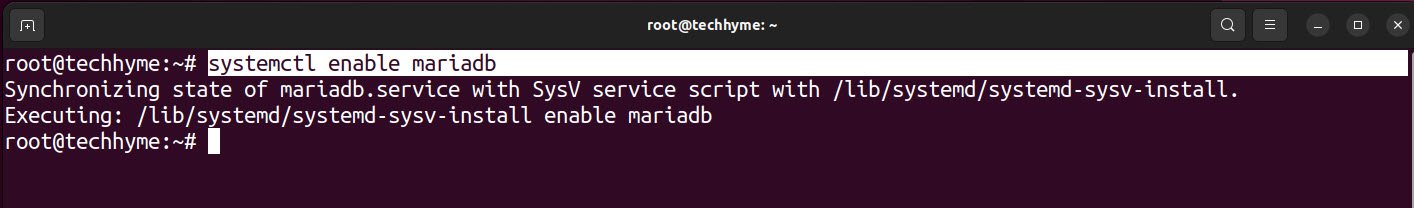
Thank You