In the rapidly evolving digital world, cybersecurity has become a critical area of concern for individuals, businesses, and governments alike. Understanding cybersecurity is no longer a specialized skill, but a necessary one for navigating the digital landscape.
This article presents a comprehensive list of the top 40 cybersecurity questions, covering a wide range of topics from cryptography and encryption to various types of cyberattacks and preventive measures. Whether you’re a seasoned IT professional, a student of cybersecurity, or just a curious individual, these questions and their detailed answers will provide valuable insights into the complex world of cybersecurity.
Let’s explore into these questions and unravel the intricacies of cybersecurity.
1. What is Cryptography?
Cryptography is the practice of securing communication and data in the presence of adversaries. It involves creating written or generated codes that allow information to be kept secret.
2. What is the difference between Symmetric and Asymmetric encryption?
Symmetric encryption uses the same key for encryption and decryption, while asymmetric encryption uses different keys (public and private keys) for encryption and decryption.
3. What is the difference between IDS and IPS?
IDS (Intrusion Detection System) is a system that monitors and detects potential intrusions or attacks but does not take action. IPS (Intrusion Prevention System), on the other hand, not only detects but also prevents identified threats.
4. What is the CIA triad and can you explain it?
The CIA triad stands for Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. It’s a model designed to guide policies for information security within an organization.
5. How is Encryption different from Hashing?
Encryption is a two-way function; what is encrypted can be decrypted with the proper key. Hashing, however, is a one-way function that scrambles plain text to produce a unique message digest.
6. What is a Firewall and why is it used?
A firewall is a network security device that monitors incoming and outgoing network traffic and decides whether to allow or block specific traffic based on a defined set of security rules.
7. What is the difference between “VA” and “PT”?
VA (Vulnerability Assessment) is the process of identifying and quantifying vulnerabilities in a system. PT (Penetration Testing) is the practice of testing a computer system, network, or web application to find vulnerabilities that an attacker could exploit.
8. What is a Three-Way Handshake?
It is a method used in a TCP/IP network to create a connection between a local host/client and server. It is a three-step method that requires both the client and server to exchange SYN and ACK (acknowledgement) packets before actual data communication begins.
9. What are the response codes that can be received from a Web Application?
Response codes are grouped into five classes: informational responses (100–199), successful responses (200–299), redirects (300–399), client error responses (400–499), and server error responses (500–599).
10. What is traceroute? Why is it used?
Traceroute is a network diagnostic tool used to track the pathway taken by a packet on an IP network from source to destination. It also records the time taken for each hop the packet makes during its route to its destination.
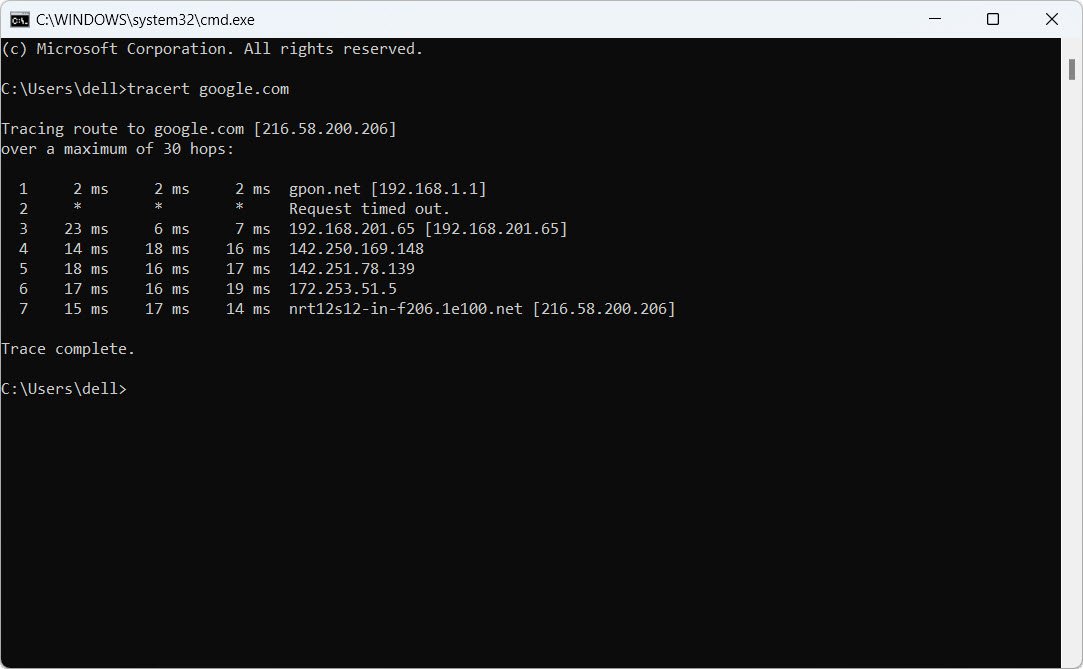
11. What is the difference between HIDS and NIDS?
HIDS (Host Intrusion Detection System) operates on a particular system (host), while NIDS (Network Intrusion Detection System) operates at the network level and monitors malicious activities on the entire network.
12. What are the steps to set up a Firewall?
Steps include defining firewall policies, setting up default deny rule, setting up public servers, configuring NAT (Network Address Translation), and testing the firewall for any vulnerabilities.
13. Can you explain SSL Encryption?
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) encryption is a security protocol that provides privacy, authentication, and integrity to Internet communications. It’s commonly used in web browsing, email, instant messaging, and voice-over-IP (VoIP).
14. What steps will you take to secure a server?
Steps include keeping the system updated, using strong and unique passwords, enabling firewall rules, disabling unnecessary services, and regularly monitoring system and network logs.
15. Can you explain Data Leakage?
Data leakage refers to the unauthorized transmission of data from within an organization to an external destination or recipient.
16. What are some common types of Cyber Attacks?
Common types include malware, phishing, man-in-the-middle attack, denial-of-service attack, SQL injection, and zero-day exploit.
17. What is a Brute Force Attack? and How can you prevent it from happening?
A brute force attack is a trial-and-error method used to obtain information such as a user password or personal identification number (PIN). It can be prevented by implementing account lockout policies, using complex passwords, and enabling two-factor authentication.
18. What is Port Scanning?
Port scanning is the process of sending packets to specific ports on a host and analyzing responses to identify open, closed, and filtered ports.
19. What are the different layers of the OSI model?
The OSI model has seven layers: Physical, Data Link, Network, Transport, Session, Presentation, and Application.
20. What is VPN and what is used for?
VPN (Virtual Private Network) extends a private network across a public network, enabling users to send and receive data across shared or public networks as if their computing devices were directly connected to the private network.
21. What do you understand by Risk, Vulnerability & Threat in a network?
– Risk: It is the potential for loss or damage when a threat exploits a vulnerability.
– Vulnerability: It is a weakness in a system or its design that could be exploited by a threat.
– Threat: It is anything that can exploit a vulnerability to breach security and cause harm to the network.
22. How can identity-theft be prevented?
Identity theft can be prevented by implementing strong password policies, using two-factor authentication, regularly updating and patching systems, and educating users about phishing and other social engineering attacks.
23. What are Black Hat, White Hat & Gray Hat Hackers?
– Black Hat Hackers: These are individuals who use their skills for illegal or malicious purposes.
– White Hat Hackers: These are ethical hackers who use their skills to find and fix security vulnerabilities.
– Gray Hat Hackers: These individuals fall somewhere in between, often acting without malicious intent but without permission.
24. How often should you perform Patch Management?
Patch management should be performed regularly as part of a proactive maintenance routine. The frequency will depend on the specific requirements and environment, but updates should be applied as soon as possible after they are released, especially for critical security patches.
25. How would you reset a password-protected BIOS configuration?
To reset a password-protected BIOS configuration, you would typically need to physically access the motherboard and reset the CMOS, which stores the BIOS password. This is usually done by moving a jumper on the motherboard or by removing the CMOS battery for a few minutes to reset the BIOS to its defaults. Note that this should only be done by a qualified technician and can have serious implications if done incorrectly.
26. Explain MITM attack and how to prevent it?
A Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attack occurs when a hacker intercepts communication between two systems. It can be prevented by using encrypted connections (like HTTPS), regularly updating and patching systems, and using security measures like two-factor authentication.
27. Explain DDoS attack and how to prevent it?
A Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack is an attempt to overwhelm a system with traffic, rendering it inaccessible. Preventive measures include using DDoS protection services, maintaining a robust network infrastructure, and having a response plan in place.
28. Explain XSS attack and how to prevent it?
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks involve injecting malicious scripts into websites viewed by users. Prevention strategies include validating and sanitizing input, implementing CSP (Content Security Policy), and using appropriate response headers.
29. What is an ARP and how does it work?
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a protocol used to map an IP address to a physical (MAC) address on a local network. It works by broadcasting a request for the MAC address associated with a specific IP address, and the device with that IP address responds with its MAC address.
30. What is port blocking within a LAN?
Port blocking within a LAN involves preventing traffic from flowing through specific ports, which can be used to prevent access to certain services or protocols.
31. What protocols fall under TCP/IP internet layer?
Protocols that fall under the TCP/IP internet layer include IP (Internet Protocol), ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol), IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol), and ARP (Address Resolution Protocol).
32. What is a Botnet?
A botnet is a network of compromised computers controlled by a malicious actor. These are often used to carry out DDoS attacks, send spam, or perform other malicious activities.
33. What are salted hashes?
Salted hashes involve adding a random value, or “salt,” to a password before hashing it. This makes it more difficult for attackers to use precomputed tables (rainbow tables) to crack the password.
34. Can you explain SSL and TLS?
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) and TLS (Transport Layer Security) are cryptographic protocols used to secure communication over a network. TLS is the successor to SSL and is currently more commonly used.
35. What is data protection in transit versus data protection at rest?
Data protection in transit involves securing data while it’s being transferred over a network, often using encryption. Data protection at rest involves securing data stored on physical media, again often using encryption.
36. What is 2FA and how can it implemented for public websites?
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) is a security measure that requires two forms of identification to access an account. It can be implemented on public websites using methods like SMS codes, email links, or authenticator apps.
37. What is Cognitive Cybersecurity?
Cognitive cybersecurity is an approach to securing systems that involves using artificial intelligence and machine learning to predict and respond to cyber threats.
38. What is the difference between VPN and VLAN?
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) is a technology that creates a secure connection over a public network, allowing remote access to a private network. A VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) is a way to group network devices together logically, regardless of their physical location.
39. Explain Phishing and how to prevent it?
Phishing is a type of attack where the attacker pretends to be a trustworthy entity to trick victims into revealing sensitive information. It can be prevented through user education, email filtering, and regularly updating and patching systems.
40. Explain SQL Injection and how to prevent it?
SQL Injection involves inserting malicious SQL code into a query, which can then be used to manipulate the database. It can be prevented by using parameterized queries, regularly updating and patching database systems, and limiting database permissions.



