Wi-Fi Adapters are devices that allow computers to connect to the Internet and to other computers without using wires. A USB WiFi adapter overrides the computer’s built-in wireless functionality, giving you a faster, more reliable connection to your available network signals through the USB port instead.
There are so many benefits of USB Wi-Fi adapter are:
- No installation needed
- Less expensive
- More connection speed (no speed lagging)
- Supports packet injection
To hack the Wi-Fi network, you need a USB wireless card which supports both Monitor Mode and Packet Injection because not all cards supports these features.
Recommended Read:
In this article, we’ll explain the method from which you can easily test the Packet Injection capability of your USB Wireless Card.
The first step is to type “iwconfig” command which is identical to “ifconfig” through which you can easily view all the details of your Wireless Adapter like SSID Name, Encryption, Tx-Power etc.
iwconfig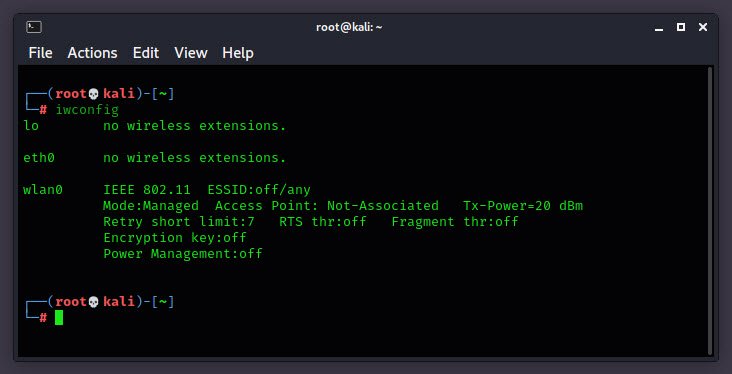
Ethernet interfaces are named eth0, eth1, whereas WiFi interfaces are named wlan0, wlan1, and so on.
Next, you need to put your wireless interface into monitor mode, which is the mode where you can capture all packets, even if they weren’t directed to your system.
To do this, you have to type the following command into your terminal which will enable the monitor mode with an interface wlan0mon.
airmon-ng start wlan0monIn case, if you want to enable the monitor mode on a specific channel i.e. on 6, then you can use “airmon-ng start wlan0 6” command.

Here you can see that, the mode is now Monitor mode.
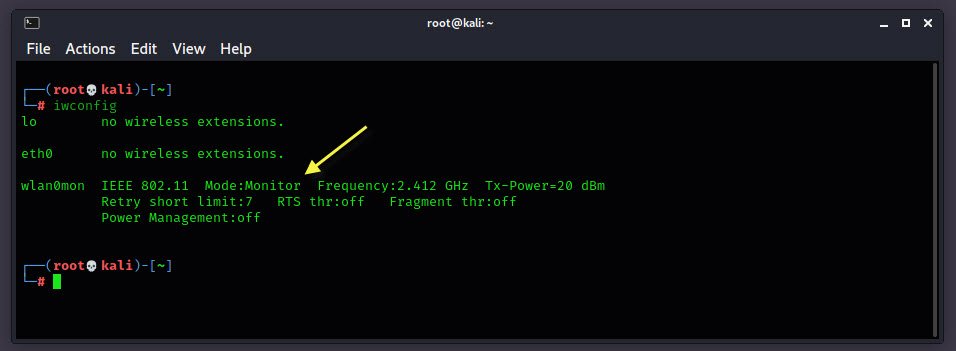
In case, if you want to stop the monitor mode, you can run “airmon-ng stop wlan0mon” command which will destroy the monitor mode interface and place the wireless interface back into managed mode.
Now here the final step comes to test the packet injection capability of your Wireless card.
The packet injection test determines if your card can successfully inject and determine the ping response times to the Access Point (AP). Type the following command to test the packet injection with Basic Test:
aireplay-ng --test wlan0mon
In above output, you can see that:
- 01:22:40 Found 2 APs: These access points (APs) were found either through the broadcast probes or received beacons.
- 01:22:42 Injection is working!: This confirms your card can inject.
For Hidden BSSID’s, you can run the following command to test packet injection:
aireplay-ng --test -e <Name> -a <BSSID> wlan0monYou can also use airserv-ng tool to test the packet injection capability as explained on Yeahhub.com.



Pingback: A to Z - Computer Security Terms and Definitions - Tech Hyme
Pingback: Wireless Issues, Types, Applications and Its Technologies - Tech Hyme
Pingback: Top 6 Different Modes of Wireless Network Adapters in Kali Linux - Tech Hyme
Pingback: Wireless Packet Injection Testing Tutorial - Yeah Hub