
Apache Tomcat is an open-source Java-based web application server that is designed to run Java servlets and JavaServer Pages (JSPs). It is developed and maintained by the Apache Software Foundation and is widely used as a production-level web server for Java-based applications.
Tomcat provides a simple, stable, and secure environment for hosting and running web applications. It provides a number of features and services that make it an ideal platform for developing and deploying web-based applications, such as:
- Servlet and JSP container: Tomcat provides a runtime environment for Java servlets and JSPs, enabling developers to create dynamic, data-driven web pages and applications.
- HTTP server: Tomcat includes a built-in HTTP server, allowing it to serve HTTP requests and responses to client browsers.
- Java Web Socket support: Tomcat provides support for the Java Web Socket API, making it easy to implement real-time, two-way communication between web applications and clients.
- Connection pooling and load balancing: Tomcat includes built-in connection pooling and load balancing capabilities, allowing applications to efficiently handle large numbers of concurrent connections and requests.
Overall, Apache Tomcat is a robust and versatile server that is widely used by developers to host and run web applications.
As you already know, Tomcat requires Java to be installed as tomcat implements Java-based technologies. To install Java, you can run the following command:
Command: apt install default-jdk

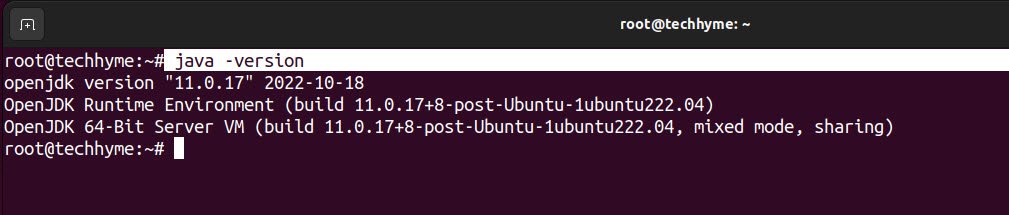
Verify if java has been installed successfully by running the below command.
Command: java -version
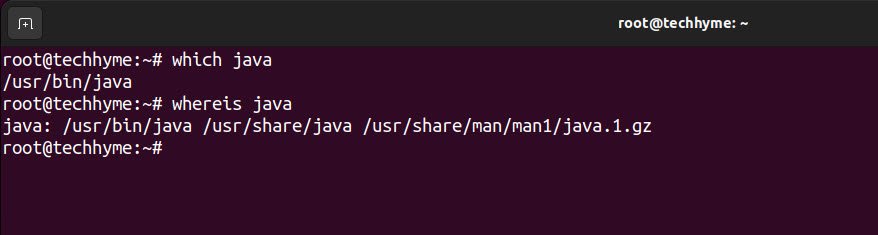
You can also check the location of java binaries using which and whereis commands.
Command: which java
Command: whereis java
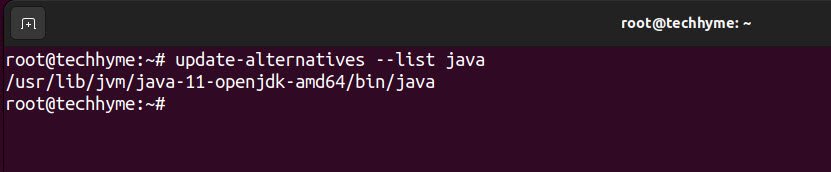
Furthermore, you can also run the following command to check the installation path of java. The system should respond with the path where Java is installed.
Command: update-alternatives –list java
Now create a folder named tomcat inside the opt directory mkdir command.
Command: cd /opt/
Command: mkdir tomcat

Download the Binary distribution of Tomcat 10 using curl command as shown below.
Command: curl -O https://dlcdn.apache.org/tomcat/tomcat-10/v10.0.27/bin/apache-tomcat-10.0.27.tar.gz

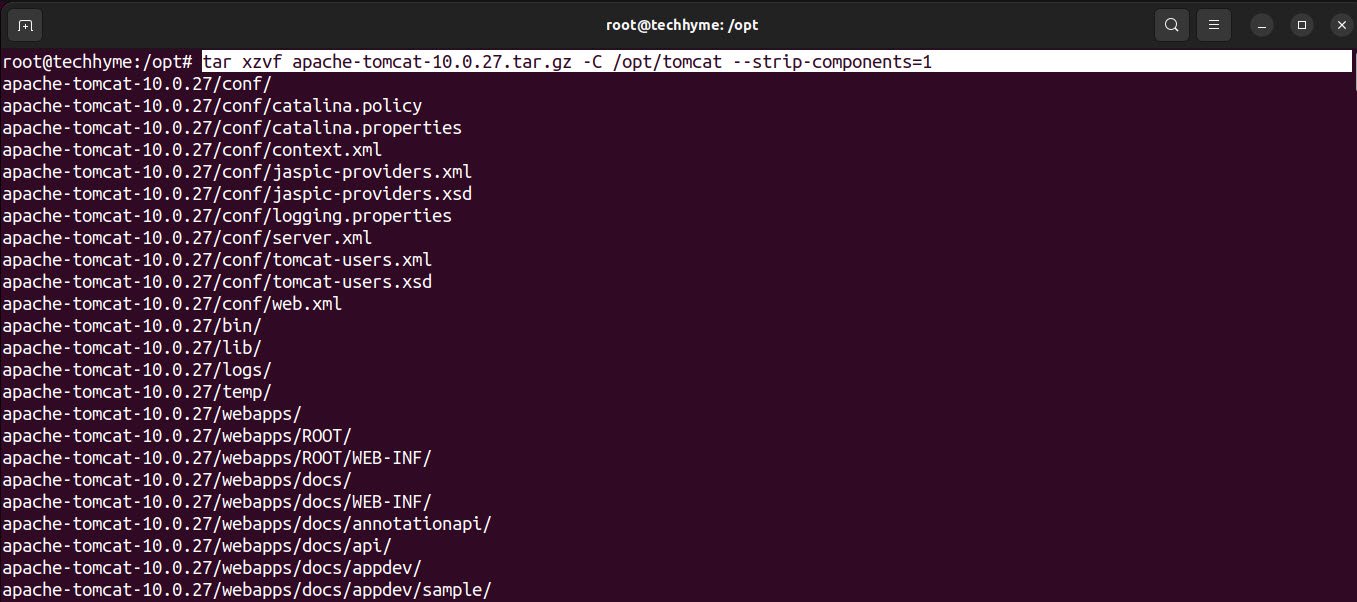
Extract the tomcat archive that you just downloaded using tar command.
Command: tar xzvf apache-tomcat-10.0.27.tar.gz -C /opt/tomcat –strip-components=1
Now that you have tomcat installed but you should consider running tomcat as a tomcat user which should be the part of tomcat group. So create a new group tomcat using groupadd command.
Command: groupadd tomcat

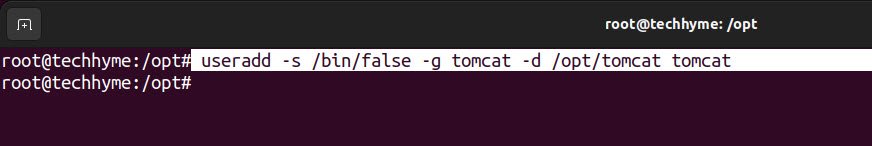
Next, create a tomcat user using useradd command and make it part of tomcat group .
Command: useradd -s /bin/false -g tomcat -d /opt/tomcat tomcat
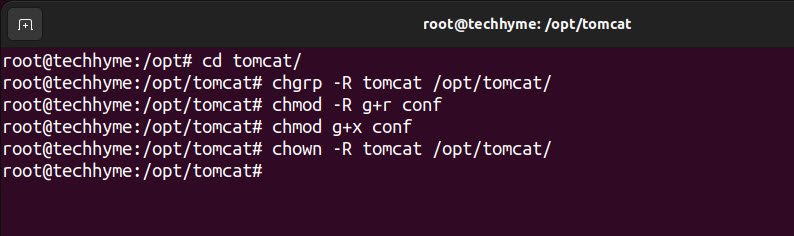
To run tomcat as tomcat user, assign the tomcat user and tomcat group to the tomcat directory by using the following commands:
Command: cd tomcat/
Command: chgrp -R tomcat /opt/tomcat/
Command: chmod -R g+r conf
Command: chmod g+x conf
Command: chown -R tomcat /opt/tomcat/
Now you are ready to start the tomcat application but it is always recommended to run the application using a service because the service saves applications to stop if the system reboots mistakenly or by any means. Let’s create the tomcat service.
Create a new file named tomcat.service as shown below in /etc/systemd/system/ directory:
Command: nano /etc/systemd/system/tomcat.service
Copy and paste the below code in tomcat.service
[Unit]
Description=Apache Tomcat
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=forking
Environment=JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-1.11.0-openjdk-amd64
Environment=CATALINA_PID=/opt/tomcat/temp/tomcat.pid
Environment=CATALINA_HOME=/opt/tomcat
Environment=CATALINA_BASE=/opt/tomcat
ExecStart=/opt/tomcat/bin/startup.sh
ExecStop=/opt/tomcat/bin/shutdown.sh
User=tomcat
Group=tomcat
UMask=0007
Restart=always
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Next, run the below commands to load the tomcat.service file & then start and enable the service.
Command: systemctl daemon-reload
Command: systemctl start tomcat
Command: systemctl enable tomcat

Verify that Tomcat is running by accessing the default welcome page in your web browser at http://localhost:8080.
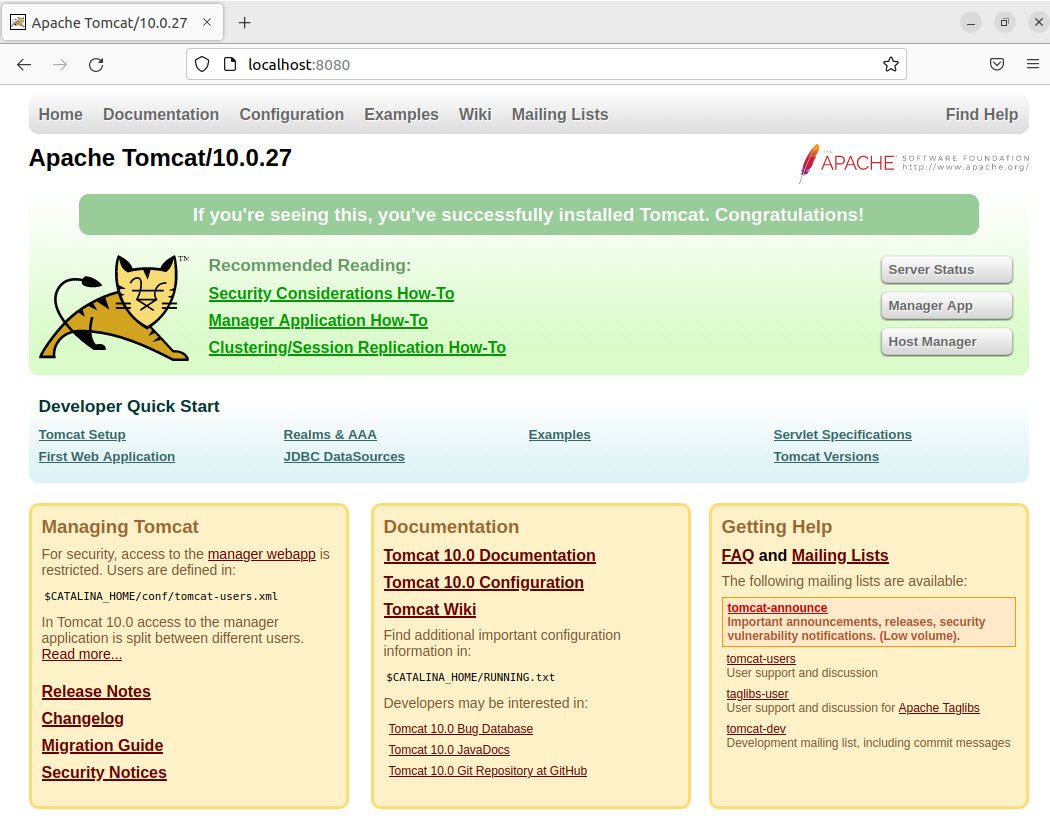
That’s it! You have successfully installed Tomcat on your Ubuntu machine.









This Post Has 3 Comments