In the realm of Linux, determining whether your system is connected to the internet is a common task. Various tools and utilities are available to perform this check, and you can use either individual commands or incorporate them into shell scripts for more comprehensive checks.
In this article, we will explore some essential Linux commands and shell scripts for checking internet connectivity.
1. Ping
a) Command:
The `ping` command sends ICMP echo requests to a target host and waits for a reply to confirm host availability over the IP network.
ping -c 1 google.com &> /dev/null && echo "Connected" || echo "Not Connected"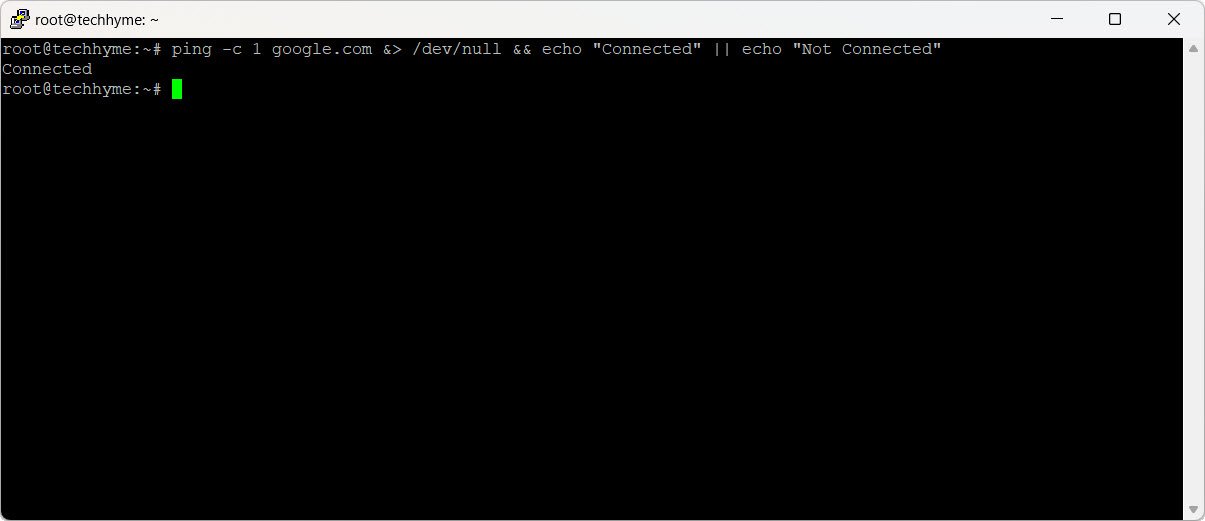
b) Shell Script:
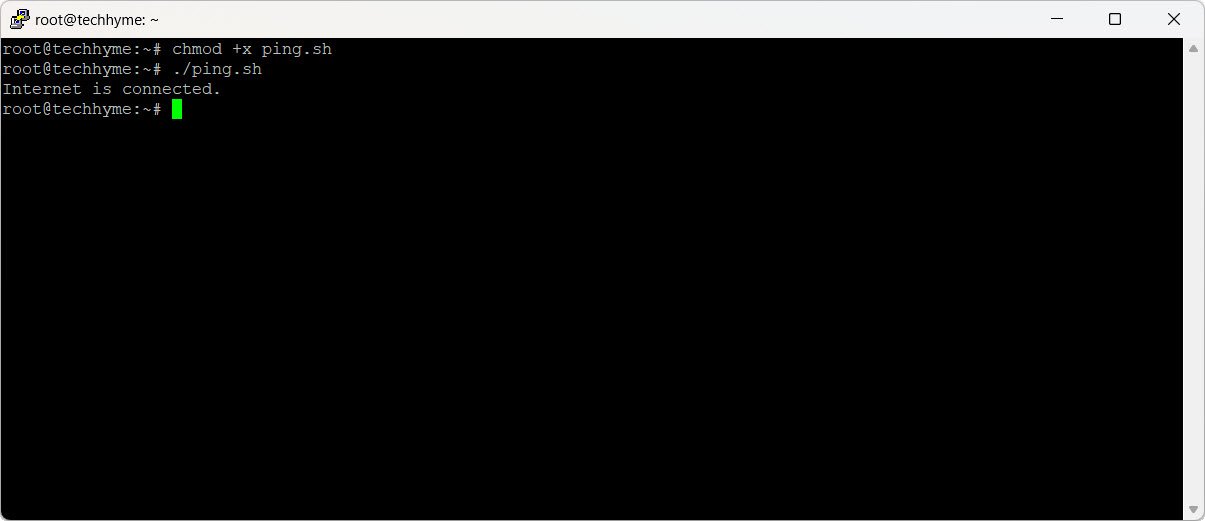
Alternatively, you can use a shell script for the same check using an if-else statement:
if ping -c 1 google.com &> /dev/null; then
echo "Internet is connected."
else
echo "No internet connection."
fi
Output:
2. Curl
a) Command:
`Curl` is a versatile tool for retrieving data from a specified URL. It can be used to check internet connectivity by accessing a web page or file.
curl -s --head http://www.google.com | grep "200 OK" &> /dev/null && echo "Connected" || echo "Not Connected"
b) Shell Script:
The same check can be incorporated into a shell script:
if curl -s --head http://www.google.com | grep "200 OK" > /dev/null; then
echo "Internet is connected."
else
echo "No internet connection."
fi
Output:

3. Wget
a) Command:
`Wget` can be used to attempt downloading a page or file from the internet, checking internet connectivity.
wget -q --spider http://google.com && echo "Connected" || echo "Not Connected"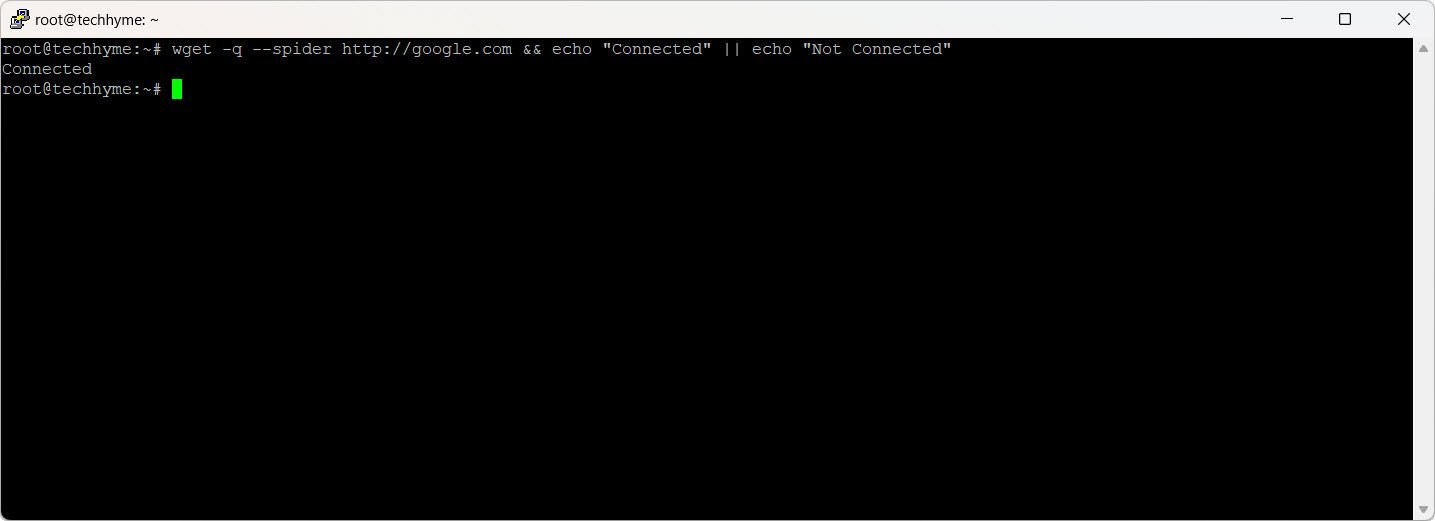
b) Shell Script:
Incorporate the `wget` command into a shell script:
if wget -q --spider http://google.com; then
echo "Internet is connected."
else
echo "No internet connection."
fi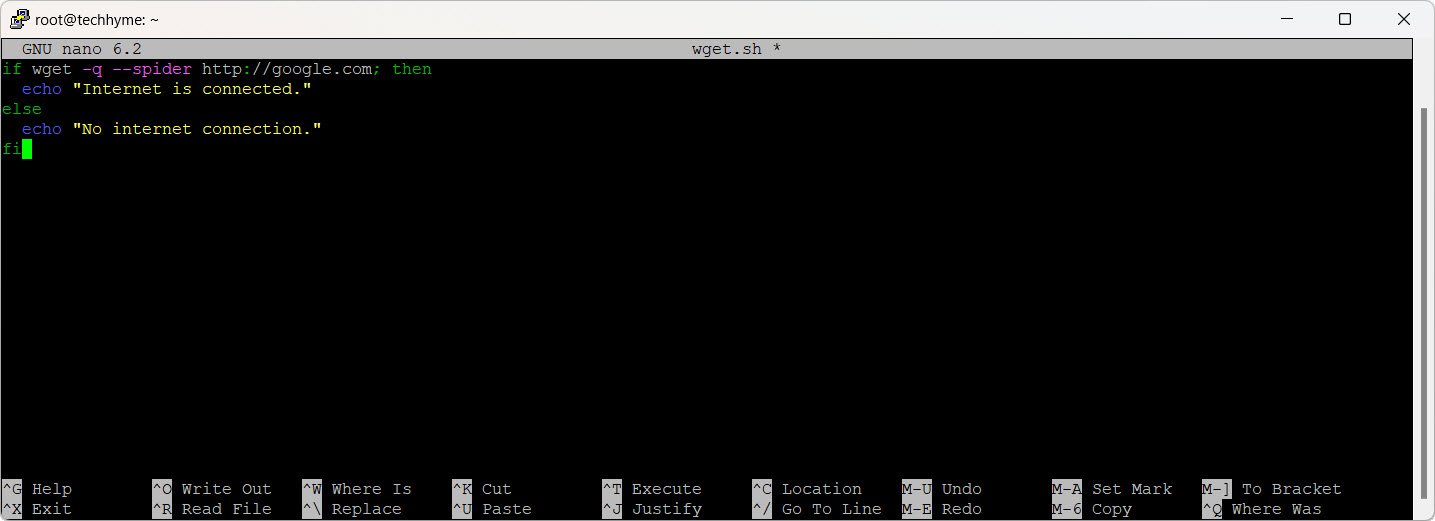
Output:
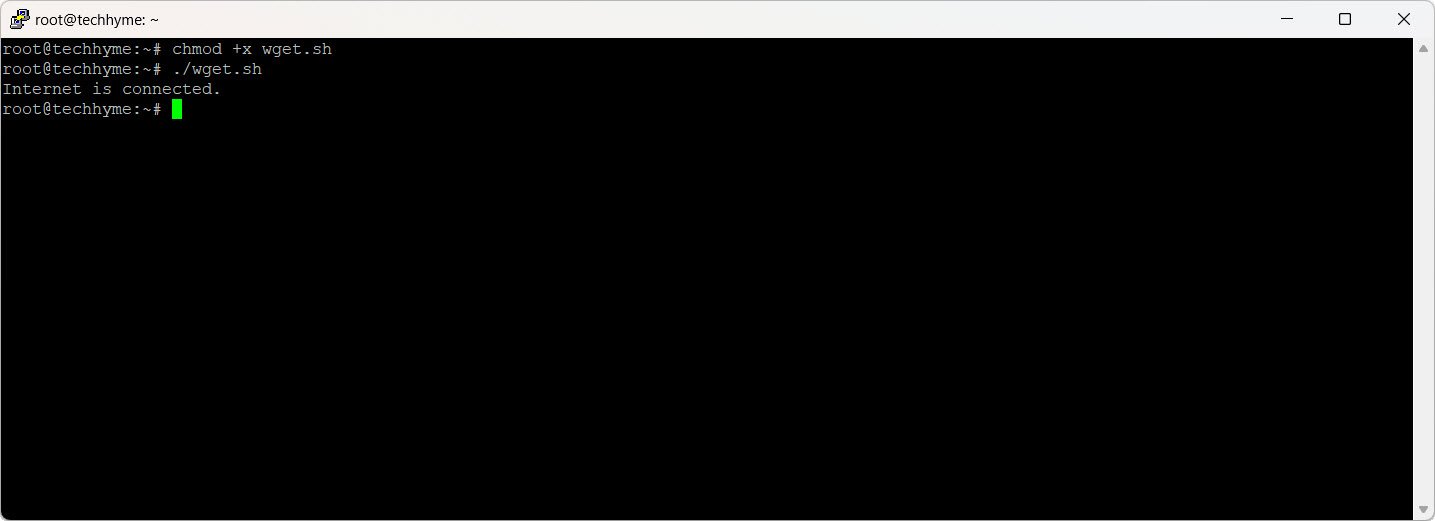
4. Netcat (nc)
a) Command:
Use `netcat` to establish TCP or UDP connections to a host port on the internet.
nc -zw1 google.com 443 && echo "Connected" || echo "Not Connected"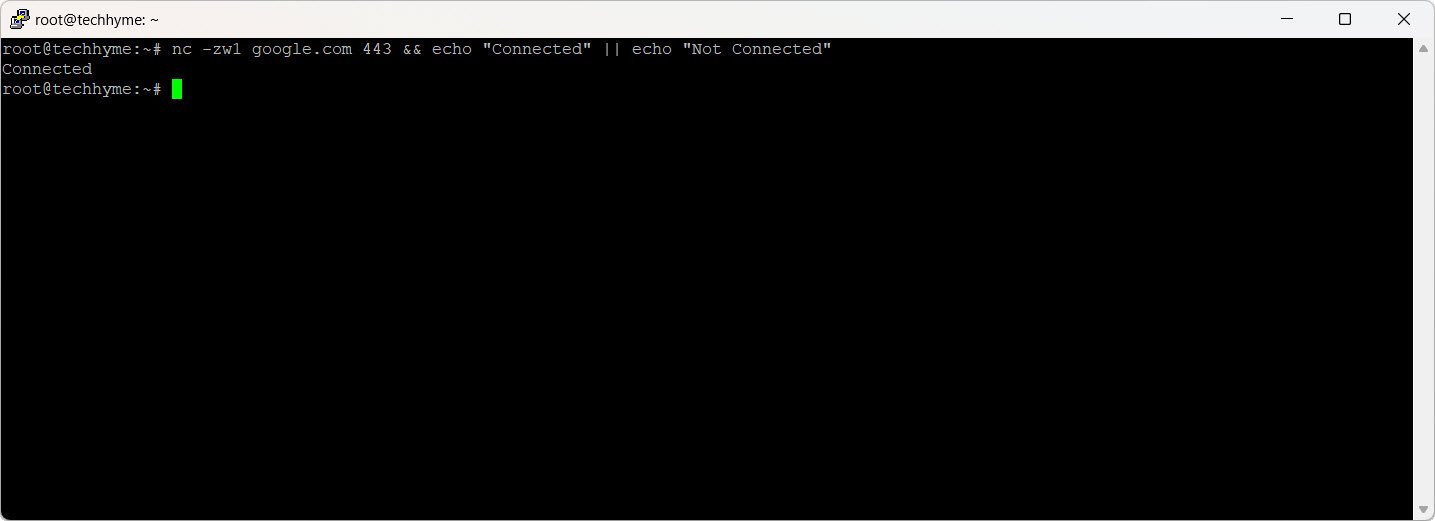
b) Shell Script:
Create a shell script using the `netcat` command:
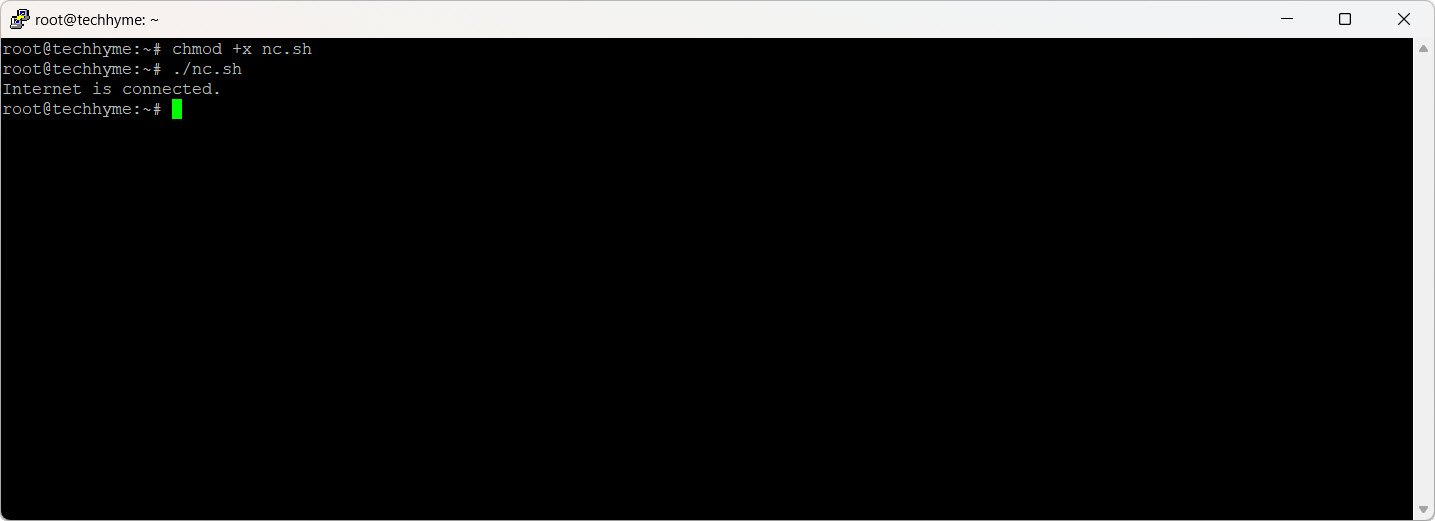
if nc -zw1 google.com 443; then
echo "Internet is connected."
else
echo "No internet connection."
fi
Output:
5. Fping
`Fping` works similarly to `ping` but can send ICMP echo requests to multiple hosts simultaneously.
a) Command:
Use `fping` to send ICMP echo requests to a destination server.
fping google.com 1>/dev/null 2>&1 && echo "Connected" || echo "Not Connected"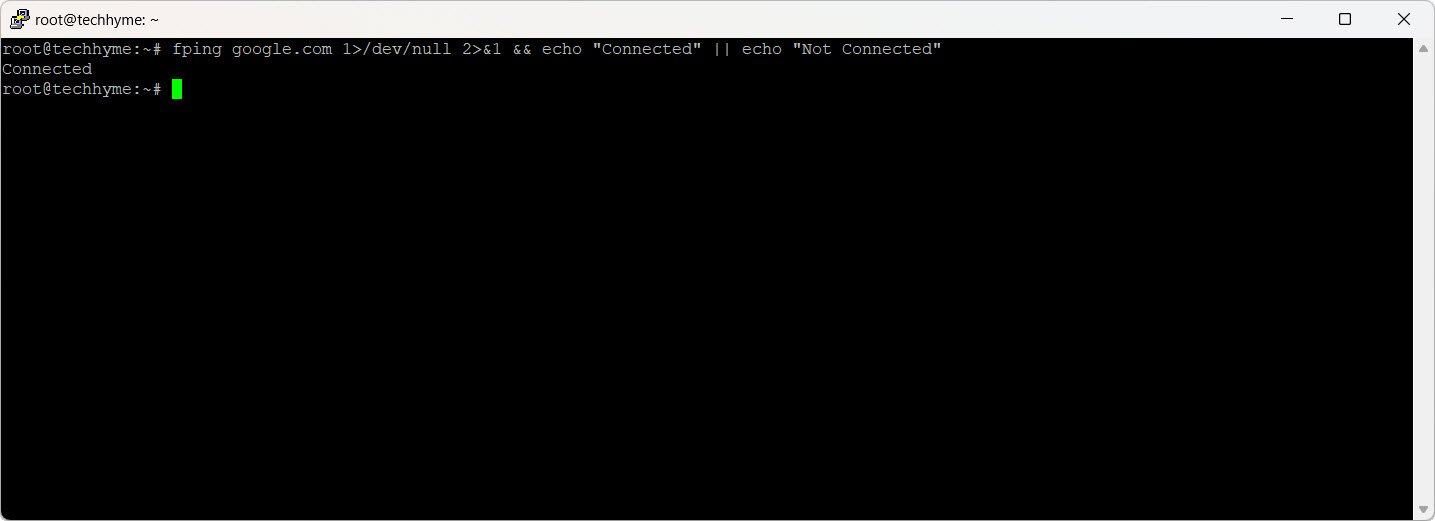
b) Shell Script:
Incorporate the `fping` command into a shell script:
if fping google.com 1>/dev/null 2>&1; then
echo "Internet is connected."
else
echo "No internet connection."
fi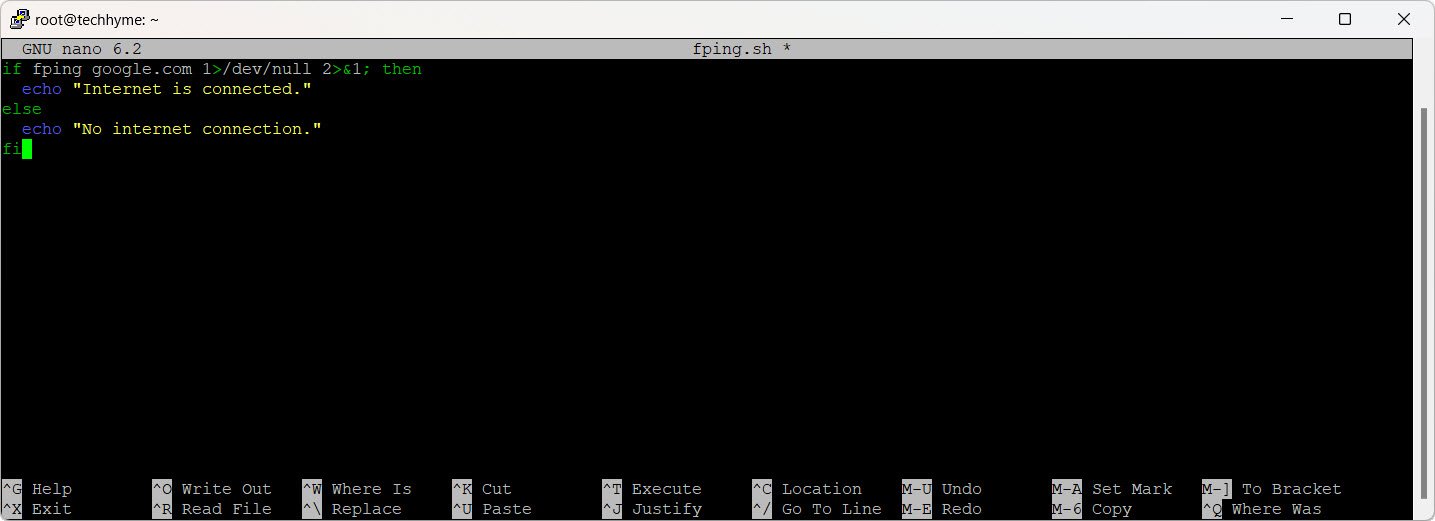
Output:
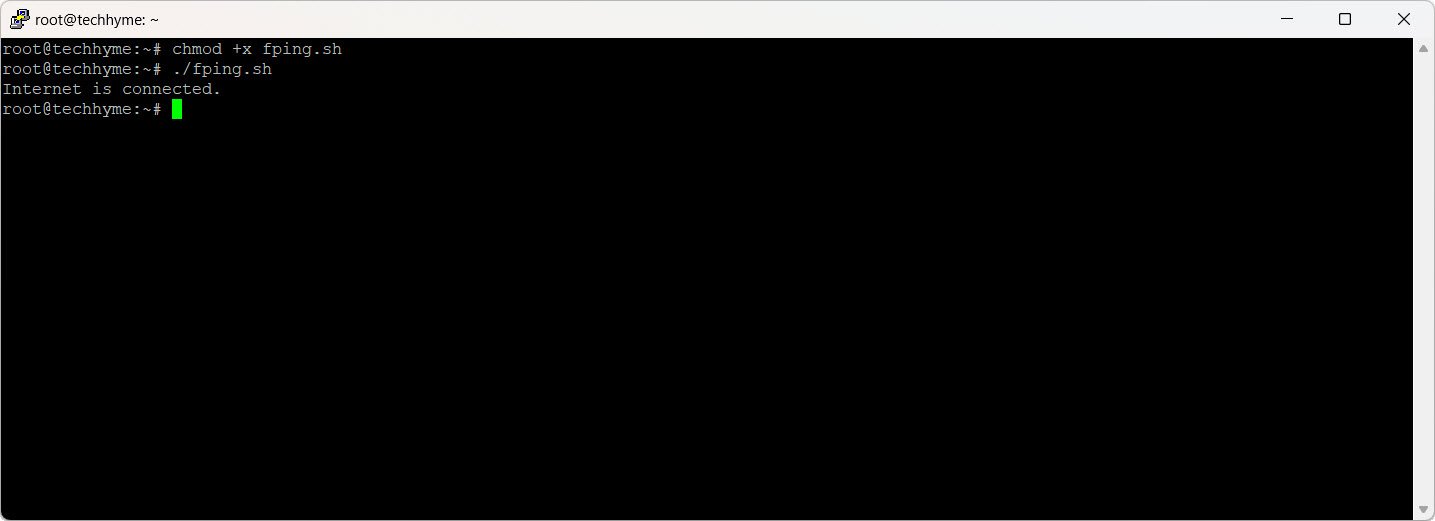
6. Ip
The `ip` command is useful for managing network interfaces and checking routing table details.
a) Command:
Check internet connectivity using the `ip` command:
ip route get 8.8.8.8 &> /dev/null && echo "Connected" || echo "Not Connected"

b) Shell Script:
Create a shell script using the `ip` command:
if ip route get 8.8.8.8 &> /dev/null; then
echo "Internet is connected."
else
echo "No internet connection."
fi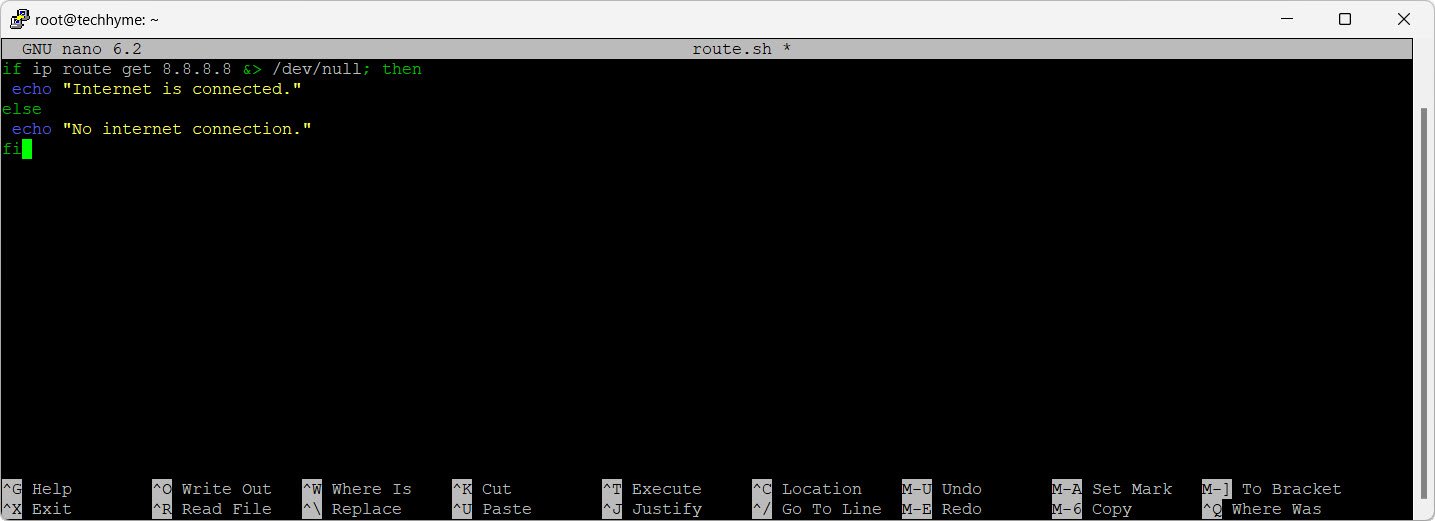
Output:
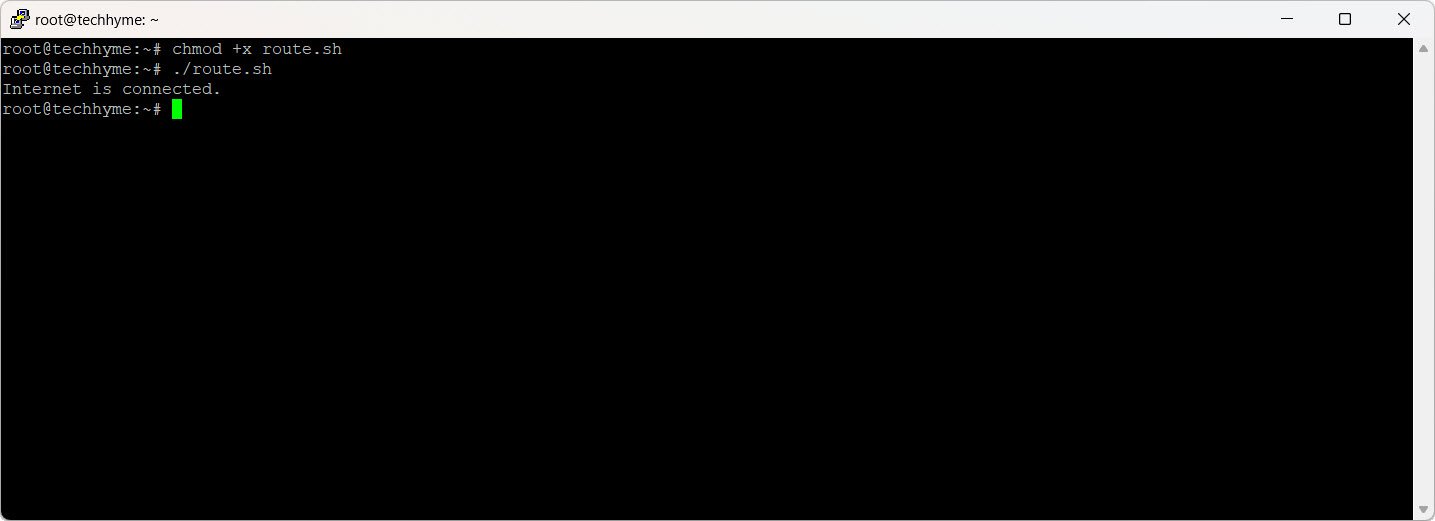
7. Nmcli
`Nmcli` (Network Manager Command Line Interface) is versatile for checking network interfaces and connections.
a) Command:
Check if the network device is in a connected state using `nmcli`:
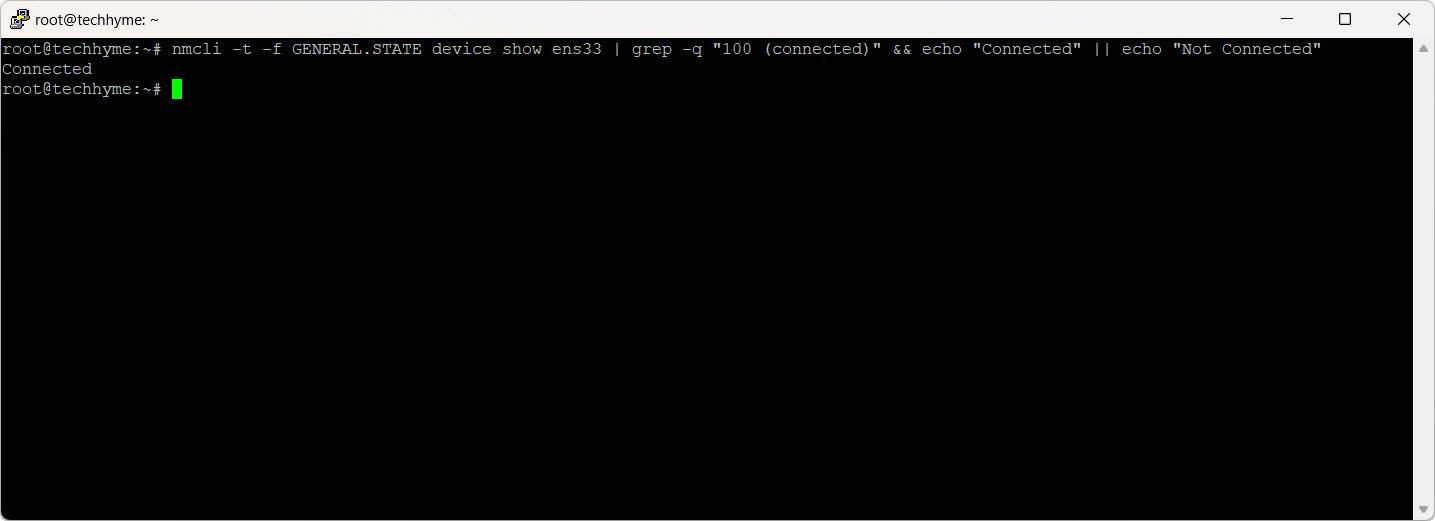
nmcli -t -f GENERAL.STATE device show ens33 | grep -q "100 (connected)" && echo "Connected" || echo "Not Connected"
b) Shell Script:
Create a shell script using the `nmcli` command:
if nmcli -t -f GENERAL.STATE device show ens33 | grep -q "100 (connected)"; then
echo "Internet is connected."
else
echo "No internet connection."
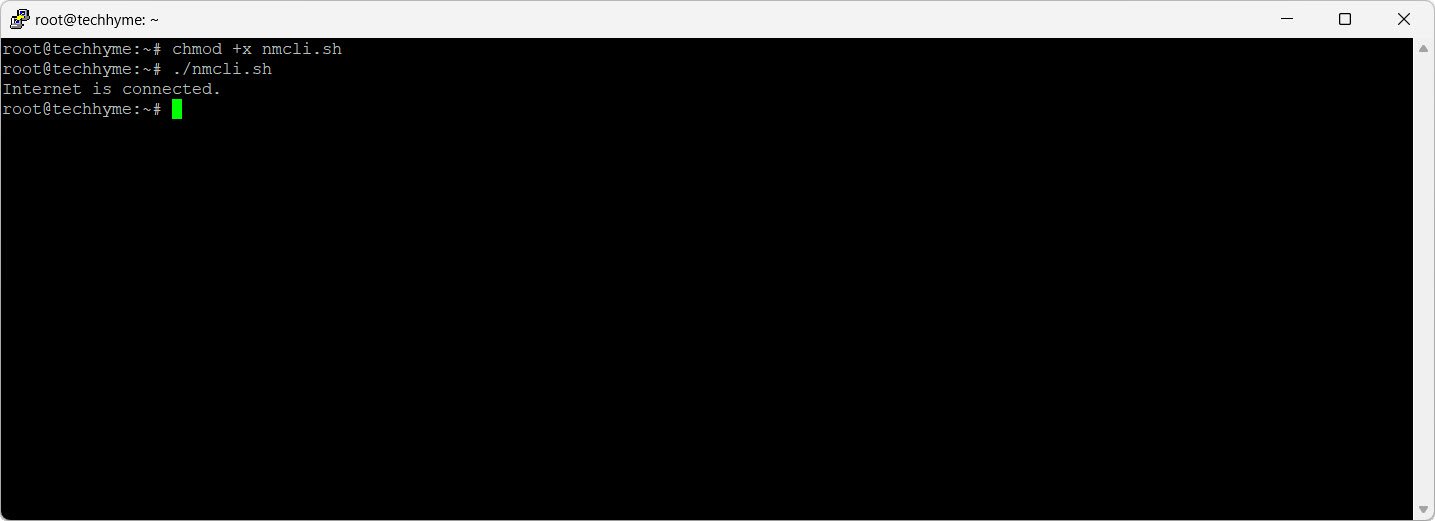
fi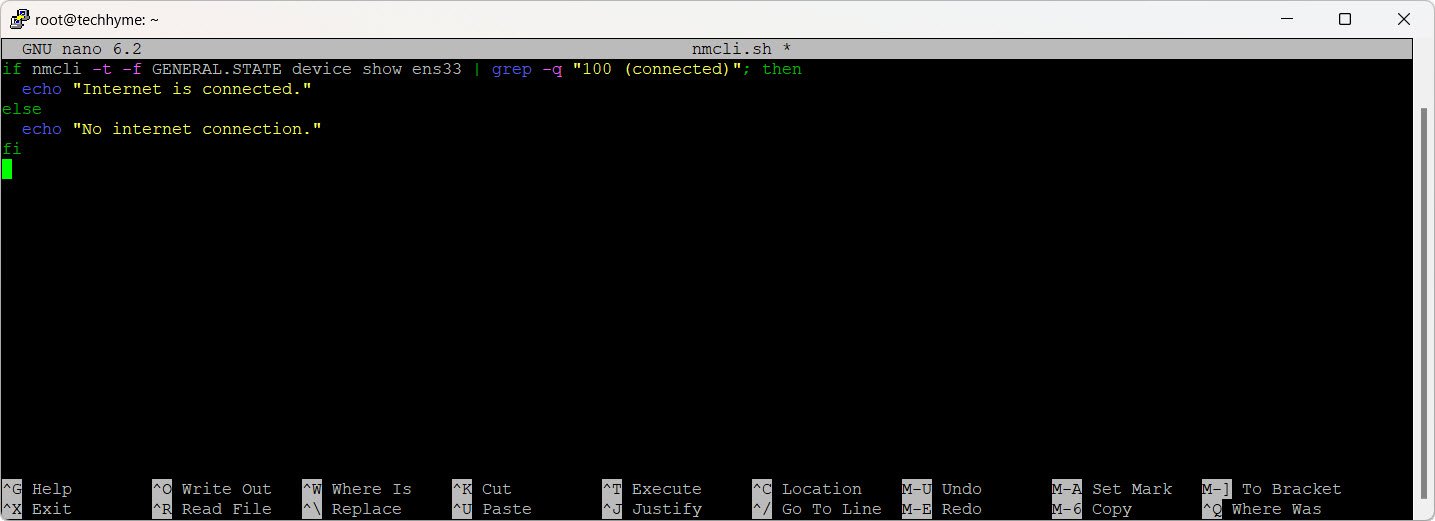
Output:
8. Dig
`Dig` (Domain Information Groper) is commonly used for querying DNS servers.
a) Command:
Check internet connectivity by querying a DNS server:
dig +short myip.opendns.com @resolver1.opendns.com > /dev/null && echo "Connected" || echo "Not Connected"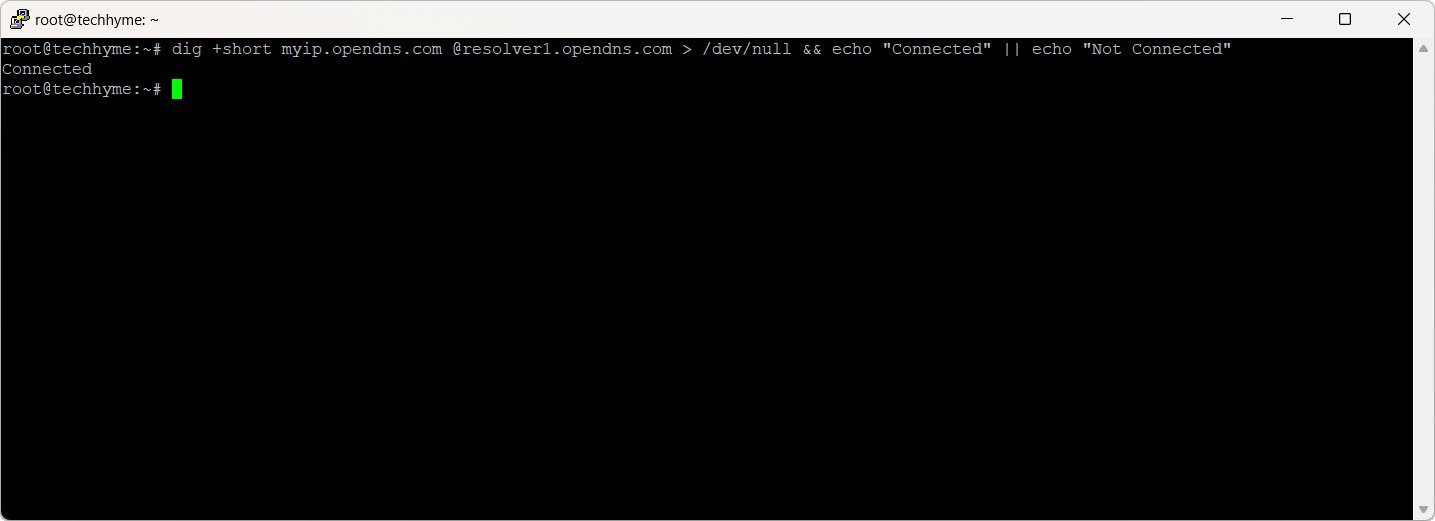
b) Shell Script:
Incorporate the `dig` command into a shell script:
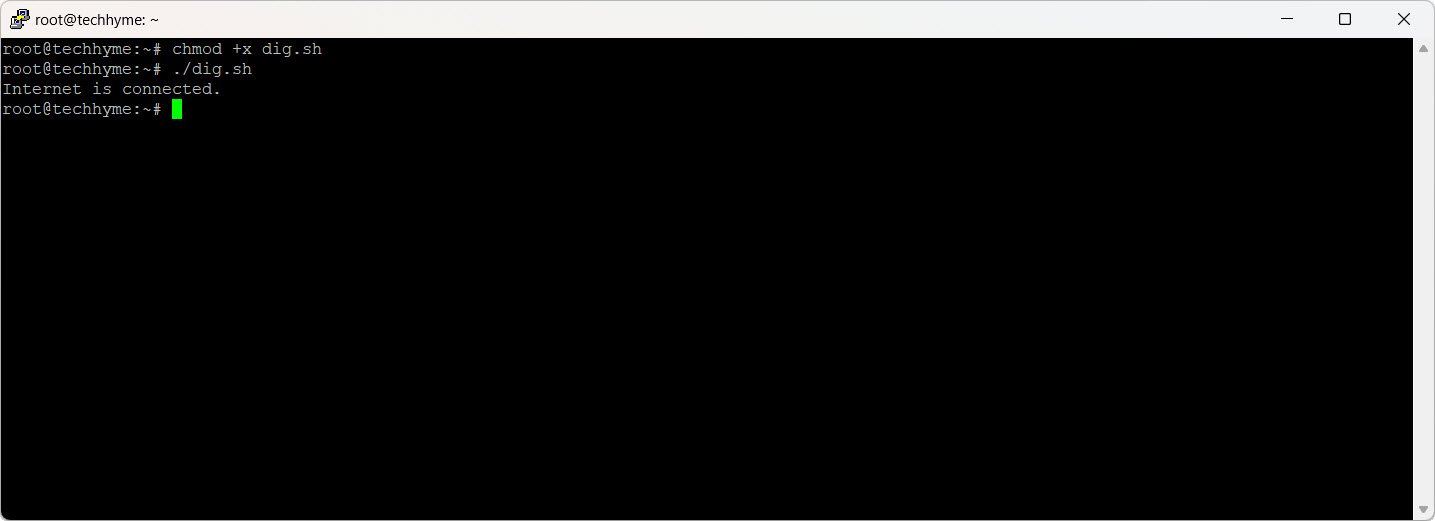
if dig +short myip.opendns.com @resolver1.opendns.com > /dev/null; then
echo "Internet is connected."
else
echo "No internet connection."
fi
Output:
9. Host
`Host` is a convenient tool for checking internet connectivity by performing DNS lookups.
a) Command:
Perform DNS lookups for a domain name using the `host` command:
host google.com > /dev/null && echo "Connected" || echo "Not Connected"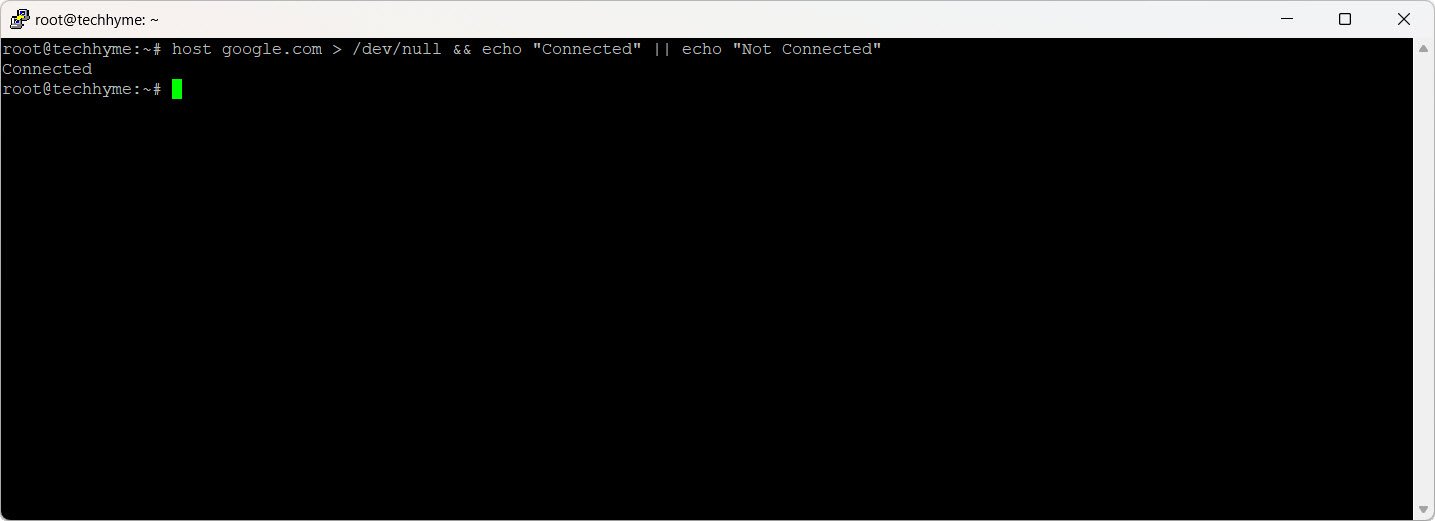
b) Shell Script:
Create a shell script using the `host` command:
if host google.com > /dev/null; then
echo "Internet is connected."
else
echo "No internet connection."
fi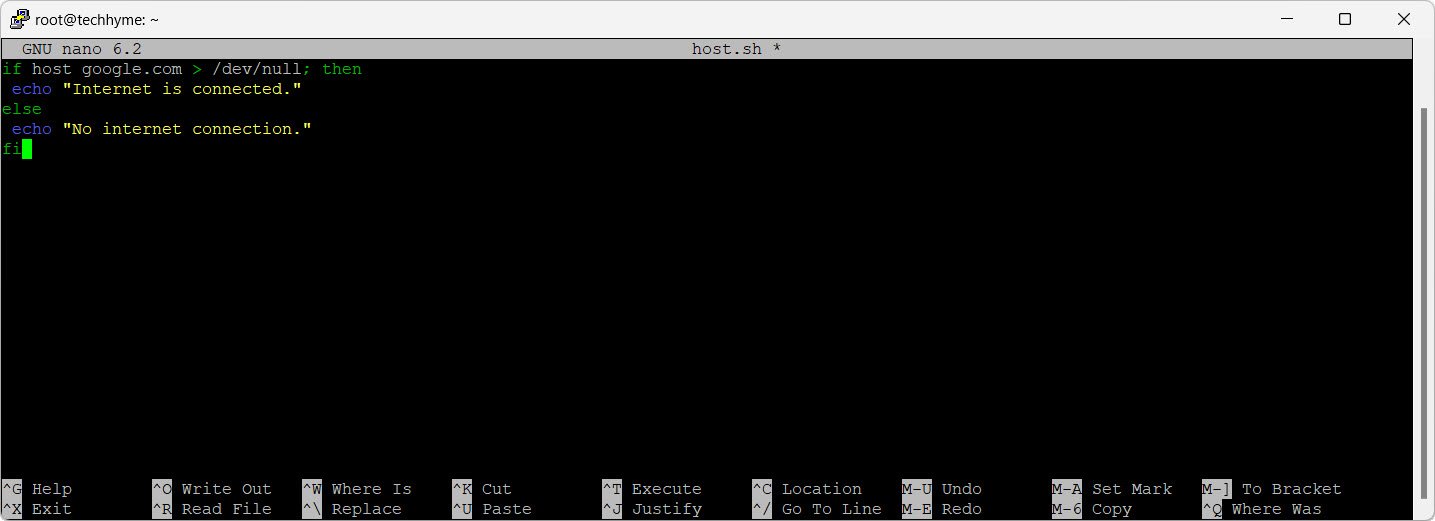
Output:
Choose the method that suits your requirements and tool availability. These commands and shell scripts provide versatile options for checking internet connectivity on Linux systems.
You may also like:- How To Install Python 2.7.18 From The Source
- How To Parse SSH Authentication Logs with Logstash
- A Comprehensive Guide to File System Commands in Linux
- Essential File Compression Commands in Linux
- Secure Shell (SSH) Protocol – A Comprehensive Guide
- Monitoring Active Connections in Kali Linux Using Netstat
- How To Easily Crack Wi-Fi Password
- 6 Most Useful Windows Command Prompt Commands
- Ripgrep – Searching for Specific File Types and Beyond
- Insert and Create Data in Elasticsearch