In many Linux environments, it’s common to grant sudo access to non-privileged users for performing administrative tasks. This practice ensures that certain actions, typically requiring root privileges, can be executed without granting full root access.
This tutorial will guide you through a step-by-step procedure to add a user to the sudoers list on Ubuntu.
Step 1: Create a New User
The first step involves creating a new user. For this example, we’ll create a user named “chetansoni.” Use the following command:
useradd -m chetansoniThe `-m` option ensures the creation of the user’s home directory if it doesn’t exist.

Step 2: Set User Password
Set a password for the newly created user using the `passwd` command:
passwd chetansoni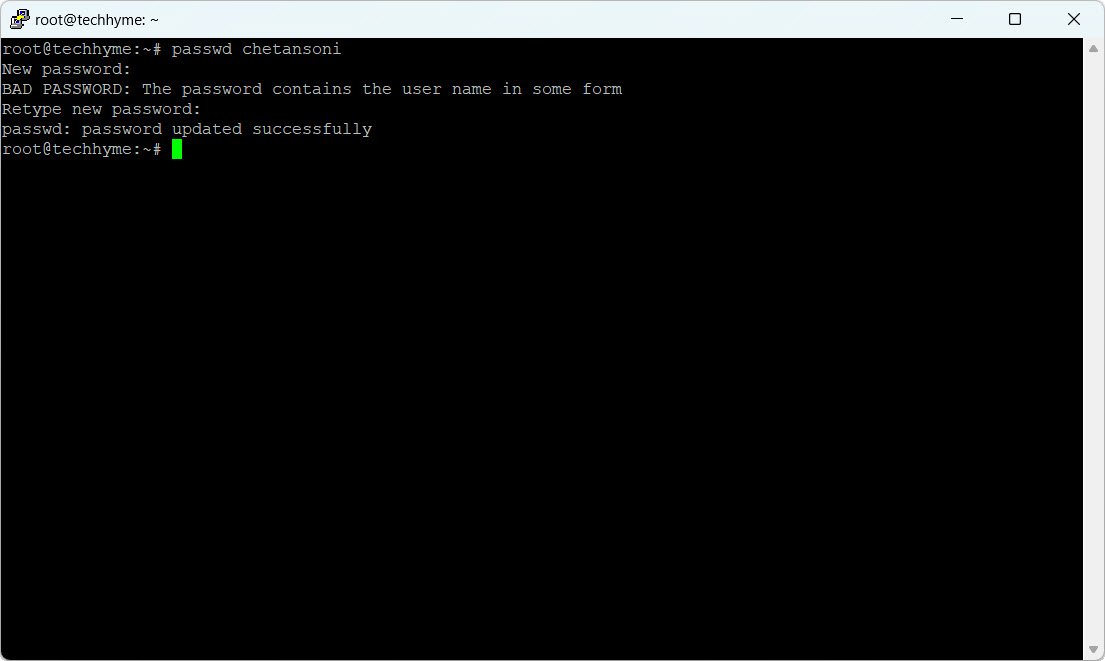
Step 3: Verify User
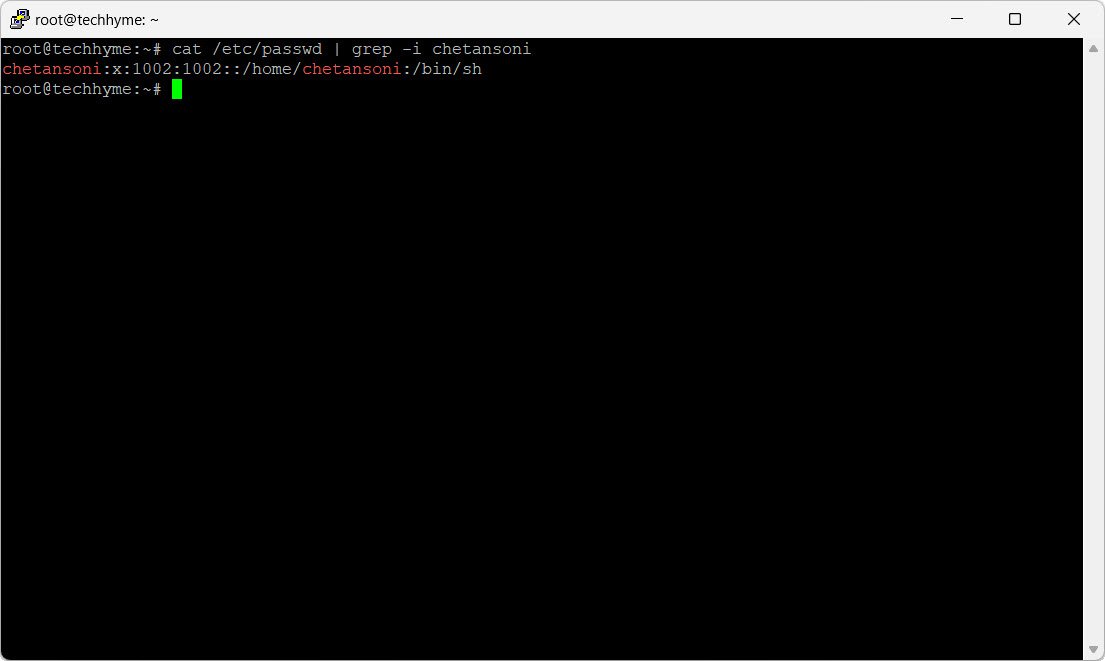
Check if the user has been successfully created by inspecting the `/etc/passwd` file:
cat /etc/passwd | grep -i chetansoniThis command will display details such as the username, user ID, group ID, and assigned shell.
Step 4: Modify User Group
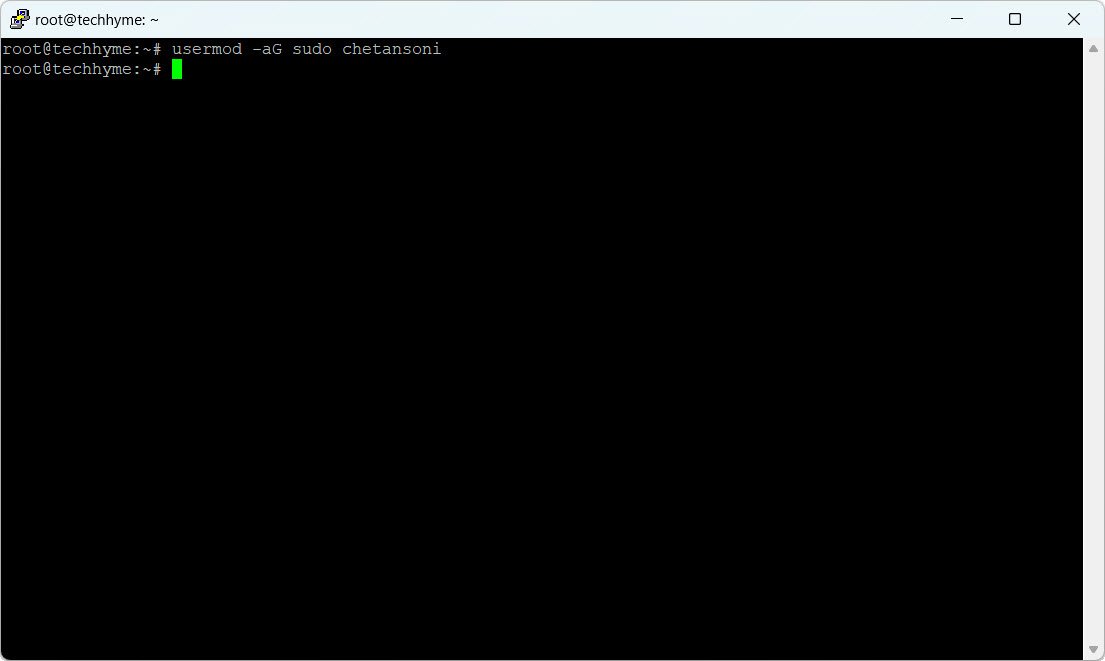
Add the user to the sudo group using the `usermod` command:
usermod -aG sudo chetansoniThis command appends the user to the supplementary group “sudo.”
Switch to the new user and verify the sudo group membership:
su - chetansoni
sudo whoami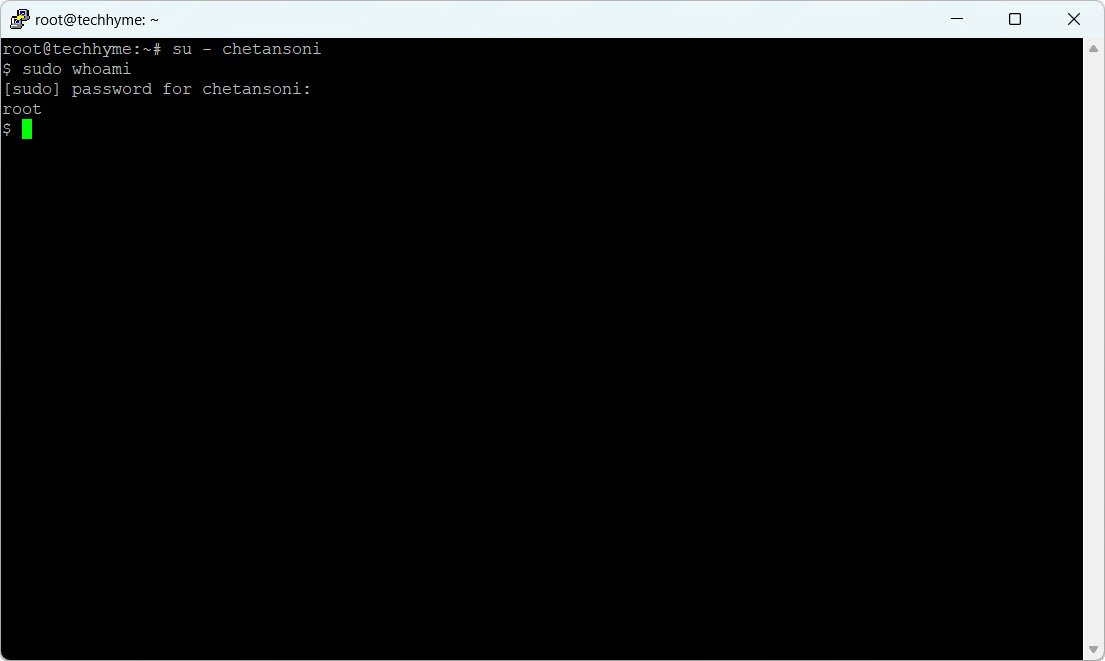
Step 5: Add User to Sudoers using visudo
While adding the user to the sudo group often suffices, it’s advisable to also add the user to the `/etc/sudoers` file. Use the `visudo` command to open the file:
visudo /etc/sudoersAdd the following line to the file:
chetansoni ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL
This line grants sudo privileges to the user “chetansoni.”
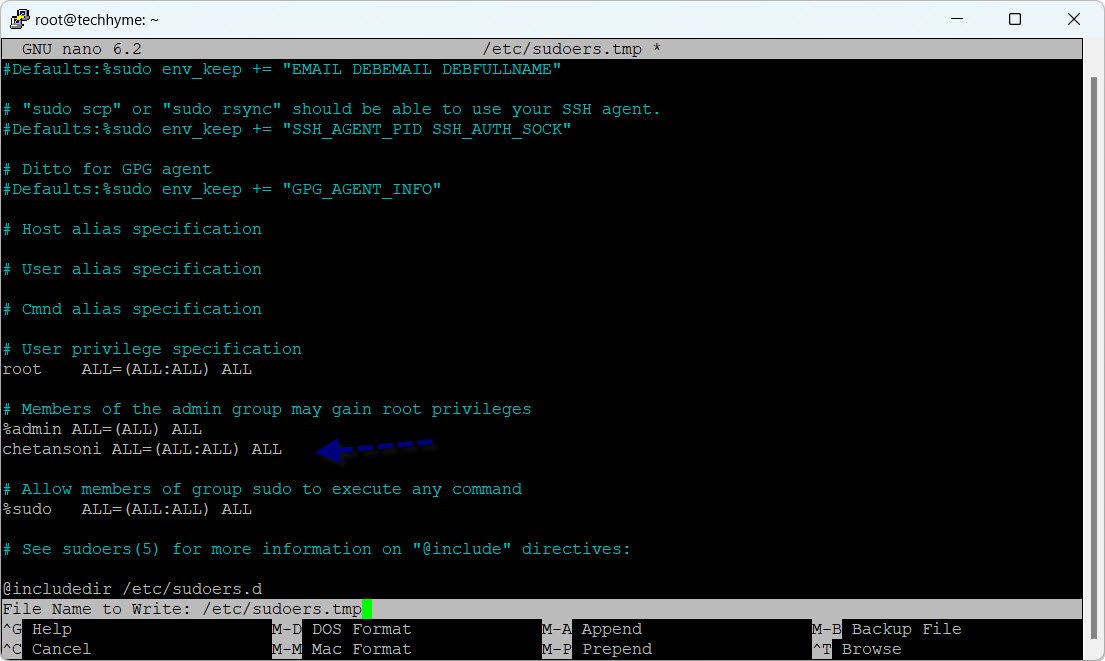
Note: Always use `visudo` to ensure there are no configuration errors in the sudoers file.
Step 6: Check Sudo Access
Finally, test sudo access by running a command that requires elevated privileges:
sudo service nginx startIf you encounter an error stating that the user is not in the sudoers file, double-check the entry in the `/etc/sudoers` file:
grep -i chetansoni /etc/sudoersFollowing these six steps will enable a non-privileged user to perform administrative tasks on Ubuntu with sudo access. Always exercise caution when modifying user privileges to ensure the security of your Linux system.
You may also like:- How To Install Python 2.7.18 From The Source
- How To Parse SSH Authentication Logs with Logstash
- A Comprehensive Guide to File System Commands in Linux
- Essential File Compression Commands in Linux
- Secure Shell (SSH) Protocol – A Comprehensive Guide
- Monitoring Active Connections in Kali Linux Using Netstat
- How To Easily Crack Wi-Fi Password
- 6 Most Useful Windows Command Prompt Commands
- Ripgrep – Searching for Specific File Types and Beyond
- Insert and Create Data in Elasticsearch