
A critical SQL injection vulnerability has been discovered in a widely used WordPress plug-in, LayerSlider, potentially compromising over 1 million sites and allowing attackers to extract sensitive data such as password hashes from associated databases.
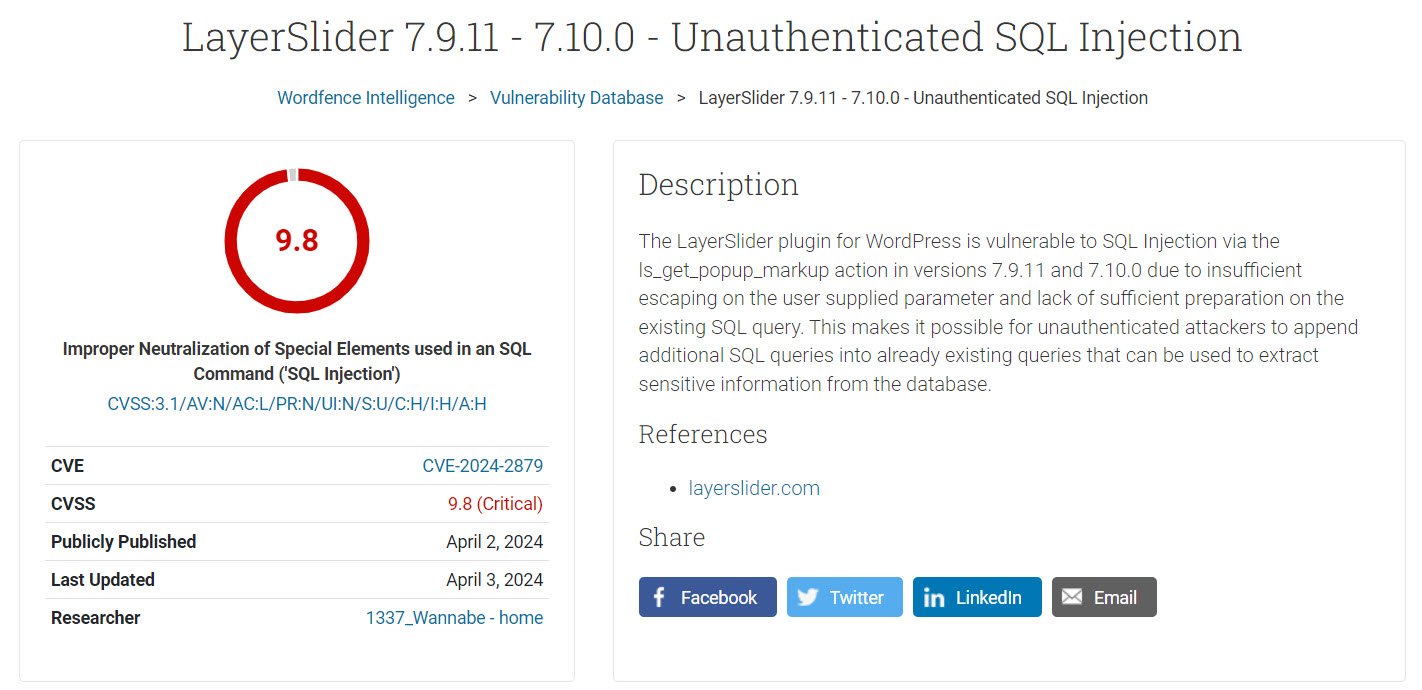
The security flaw, identified as CVE-2024-2879, was discovered by a security researcher known as AmrAwad (aka 1337_Wannabe). The vulnerability has a severity rating of 9.8 out of 10 on the CVSS 3.0 vulnerability-severity scale. It is associated with the “ls_get_popup_markup” action in versions 7.9.11 and 7.10.0 of LayerSlider.
The vulnerability arises due to “insufficient escaping on the user-supplied parameter and lack of sufficient preparation on the existing SQL query,” according to Wordfence.
This flaw allows unauthenticated attackers to append additional SQL queries into already existing queries, which can be used to extract sensitive information from the database. For his discovery, Wordfence awarded AmrAwad a bounty of $5,500, the company’s highest bounty to date. The Kreatura Team, developers of the plug-in, were notified of the flaw and delivered a patch in version 7.10.1 of LayerSlider on March 27.
The potential for exploitation of the vulnerability lies in the insecure implementation of the LayerSlider plug-in’s slider popup markup query functionality, which has an “id” parameter. If the ‘id’ parameter is not a number, it is passed without sanitization to the find() function in the LS_Sliders class.
This function queries the sliders in a way that constructs a statement without the prepare() function, which would normally parameterize and escape the SQL query for safe execution in WordPress, thereby providing protection against SQL injection attacks.
To exploit the flaw, attackers would need to use a “time-based blind approach” to extract database information. This involves using SQL CASE statements along with the SLEEP() command while observing the response time of each request to steal information from the database.
Given the widespread use of WordPress across the Internet, vulnerable WordPress sites are a popular target for attackers. Often, vulnerabilities exist in plug-ins that independent developers create for adding functionality to sites using the platform. At least 43% of websites on the entire Internet use WordPress to power their sites, e-commerce applications, and communities. The wealth of sensitive data such as user passwords and payment info often stored within their pages represents a significant opportunity for threat actors who seek to misuse it.
Making the WordPress ecosystem more secure ultimately makes the entire web more secure. Wordfence advised that WordPress users with LayerSlider installed on sites verify immediately that they are updated to the latest, patched version of the plug-in to ensure it isn’t vulnerable to exploit.
You may also like:- Extracting .wpress Files with Wpress-Extractor
- Hackers Exploit Severe WordPress Plugin Vulnerability
- Best WordPress SEO Plugins for Enhanced Website Rankings in 2024
- 3 Best WordPress Plugins to Stop Clickjacking
- WordPress Security Checklist – 2024 Updated List
- 22 Important Key Terms Used in WordPress Website Development
- How to Prevent Malware Attacks on WordPress
- Adding a New Admin User to WordPress
- How To Force User To Login Into WordPress With Username
- Hide Your WordPress Login Error Message – A Brief Guide









This Post Has One Comment